Effects of NSAIDs on the Release of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Prostaglandin E2 from Rat Trigeminal Ganglia
- PMID: 29209105
- PMCID: PMC5676472
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9547056
Effects of NSAIDs on the Release of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Prostaglandin E2 from Rat Trigeminal Ganglia
Abstract
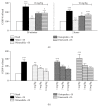
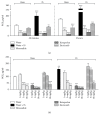
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently used to treat migraine, but the mechanisms of their effects in this pathology are not fully elucidated. The trigeminal ganglia and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) have been implicated in the pathophysiology of migraine. The release of CGRP and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) from freshly isolated rat trigeminal ganglia was evaluated after oral administration of nimesulide, etoricoxib, and ketoprofen, NSAIDs with different pharmacological features. Thirty minutes after oral administration, nimesulide, 10 mg/Kg, decreased the GCRP release induced by an inflammatory soup, while the other NSAIDs were ineffective at this point in time. Two hours after oral nimesulide (5 and 10 mg/Kg) and ketoprofen (10 mg/Kg), but not of etoricoxib, a significant decrease in the CGRP release was observed. All drugs reduced PGE2, although with some differences in timing and doses, and the action on CGRP does not seem to be related to PGE2 inhibition. The reduction of CGRP release from rat trigeminal ganglia after nimesulide and ketoprofen may help to explain the mechanism of action of NSAIDs in migraine. Since at 30 minutes only nimesulide was effective in reducing CGRP release, these results suggest that this NSAID may exert a particularly rapid effect in patients with migraine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methylprednisolone blocks interleukin 1 beta induced calcitonin gene related peptide release in trigeminal ganglia cells.J Headache Pain. 2016;17:19. doi: 10.1186/s10194-016-0609-x. Epub 2016 Mar 1. J Headache Pain. 2016. PMID: 26931452 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β stimulates COX-2 dependent PGE₂ synthesis and CGRP release in rat trigeminal ganglia cells.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 4;6(3):e17360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017360. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21394197 Free PMC article.
-
An in vivo rat model to study calcitonin gene related peptide release following activation of the trigeminal vascular system.Pain. 2001 May;92(1-2):101-6. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00475-9. Pain. 2001. PMID: 11323131
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and migraine.Headache. 2006 Jun;46 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S3-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00483.x. Headache. 2006. PMID: 16927957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Trigeminovascular Pathway: Role of CGRP and CGRP Receptors in Migraine.Headache. 2017 May;57 Suppl 2:47-55. doi: 10.1111/head.13081. Headache. 2017. PMID: 28485848 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential medication overuse risk of novel anti-migraine therapeutics.Brain. 2020 Sep 1;143(9):2681-2688. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa211. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32810212 Free PMC article.
-
TRP Channels in the Focus of Trigeminal Nociceptor Sensitization Contributing to Primary Headaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 4;21(1):342. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010342. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31948011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential predictors for the efficacy of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with migraine.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 May;31(5):692-697. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.03.010. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37181139 Free PMC article.
-
L-Carnitine potentiates the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of diclofenac sodium in an experimentally-induced knee osteoarthritis rat model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Aug;23(8):1035-1044. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.43136.10138. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32952950 Free PMC article.
-
New Substituted 5-Benzylideno-2-Adamantylthiazol[3,2-b][1,2,4]Triazol-6(5H)ones as Possible Anti-Inflammatory Agents.Molecules. 2021 Jan 27;26(3):659. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030659. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33513963 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

