Palmitate induces fat accumulation by activating C/EBPβ-mediated G0S2 expression in HepG2 cells
- PMID: 29209111
- PMCID: PMC5703930
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7705
Palmitate induces fat accumulation by activating C/EBPβ-mediated G0S2 expression in HepG2 cells
Abstract
Aim: To determine the role of G0/G1 switch gene 2 (G0S2) and its transcriptional regulation in palmitate-induced hepatic lipid accumulation.
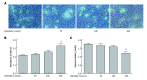
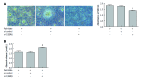
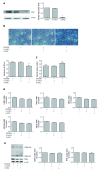
Methods: HepG2 cells were treated with palmitate, or palmitate in combination with CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP)β siRNA or G0S2 siRNA. The mRNA expression of C/EBPβ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ and PPARγ target genes (G0S2, GPR81, GPR109A and Adipoq) was examined by qPCR. The protein expression of C/EBPβ, PPARγ, and G0S2 was determined by Western blotting. Lipid accumulation was detected with Oil Red O staining and quantified by absorbance value of the extracted Oil Red O dye. Lipolysis was evaluated by measuring the amount of glycerol released into the medium.
Results: Palmitate caused a dose-dependent increase in lipid accumulation and a dose-dependent decrease in lipolysis in HepG2 cells. In addition, palmitate increased the mRNA expression of C/EBPβ, PPARγ, and PPARγ target genes (G0S2, GPR81, GPR109A, and Adipoq) and the protein expression of C/EBPβ, PPARγ, and G0S2 in a dose-dependent manner. Knockdown of C/EBPβ decreased palmitate-induced PPARγ and its target genes (G0S2, GPR81, GPR109A, and Adipoq) mRNA expression and palmitate-induced PPARγ and G0S2 protein expression in HepG2 cells. Knockdown of C/EBPβ also attenuated lipid accumulation and augmented lipolysis in palmitate-treated HepG2 cells. G0S2 knockdown attenuated lipid accumulation and augmented lipolysis, while G0S2 knockdown had no effects on the mRNA expression of C/EBPβ, PPARγ, and PPARγ target genes (GPR81, GPR109A and Adipoq) in palmitate-treated HepG2 cells.
Conclusion: Palmitate can induce lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells by activating C/EBPβ-mediated G0S2 expression.
Keywords: Adipogenesis; CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β; G0/G1 switch gene 2; Lipolysis; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Obesity; Proliferator-activated receptor γ; Saturated fatty acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures


References
-
- Cacicedo JM, Benjachareowong S, Chou E, Ruderman NB, Ido Y. Palmitate-induced apoptosis in cultured bovine retinal pericytes: roles of NAD(P)H oxidase, oxidant stress, and ceramide. Diabetes. 2005;54:1838–1845. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

