Combined endovascular brachytherapy, sorafenib, and transarterial chemobolization therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal vein tumor thrombus
- PMID: 29209114
- PMCID: PMC5703933
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7735
Combined endovascular brachytherapy, sorafenib, and transarterial chemobolization therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal vein tumor thrombus
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of combined endovascular brachytherapy (EVBT), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and sorafenib to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with main portal vein tumor thrombus (MPVTT).
Methods: This single-center retrospective study involved 68 patients with unresectable HCC or those who were unfit for liver transplantation and percutaneous frequency ablation according to the BCLC classification. All patients had Child-Pugh classification grade A or B, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0-2, and MPVTT. The patients received either EVBT with stent placement, TACE, and sorafenib (group A, n = 37), or TACE with sorafenib (group B, n = 31). The time to progression (TTP) and overall survival (OS) were evaluated by propensity score analysis.
Results: In the entire cohort, the 6-, 12-, and 24-mo survival rates were 88.9%, 54.3%, and 14.1% in group A, and 45.8%, 0%, and 0% in group B, respectively (P < 0.001). The median TTP and OS were significantly longer in group A than group B (TTP: 9.0 mo vs 3.4 mo, P < 0.001; OS: 12.3 mo vs 5.2 mo, P < 0.001). In the propensity score-matched cohort, the median OS was longer in group A than in group B (10.3 mo vs 6.0 mo, P < 0.001). Similarly, the median TTP was longer in group A than in group B (9.0 mo vs 3.4 mo, P < 0.001). Multivariate Cox analysis revealed that the EVBT combined with stent placement, TACE, and sorafenib strategy was an independent predictor of favorable OS (HR = 0.18, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: EVBT combined with stent placement, TACE, and sorafenib might be a safe and effective palliative treatment option for MPVTT.
Keywords: Endovascular brachytherapy; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Main portal vein tumor thrombus; Sorafenib; Transarterial chemoembolization.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
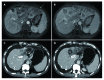
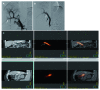
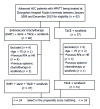
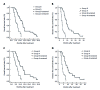
Similar articles
-
Comparison of chemoembolization with and without radiation therapy and sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a propensity score analysis.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015 Mar;26(3):320-9.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.10.019. Epub 2015 Jan 19. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25612807
-
Comprehensive treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in major portal vein.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 7;22(13):3632-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3632. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27053855 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular brachytherapy combined with stent placement and TACE for treatment of HCC with main portal vein tumor thrombus.Hepatol Int. 2016 Jan;10(1):185-95. doi: 10.1007/s12072-015-9663-8. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Hepatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26341514
-
Efficacy of sorafenib plus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in treating hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: A meta-analysis.Acta Pharm. 2024 Sep 14;74(3):405-422. doi: 10.2478/acph-2024-0019. Print 2024 Sep 1. Acta Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39279524
-
I125 irradiation stent for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: A meta-analysis.Cancer Radiother. 2021 Jun;25(4):340-349. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2020.12.003. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Cancer Radiother. 2021. PMID: 33455874
Cited by
-
Gastrointestinal side effects in hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving transarterial chemoembolization: a meta-analysis of 81 studies and 9495 patients.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;17:17588359251316663. doi: 10.1177/17588359251316663. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39926261 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization combined with helical iodine-125 seed implant, lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitors in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma complicated by main portal vein tumor thrombus: a retrospective study.Front Oncol. 2025 May 8;15:1514375. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1514375. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40406260 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying optimal therapies in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Oct 25;7:38. doi: 10.21037/tgh-20-318. eCollection 2022. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36300147 Free PMC article.
-
Combined DeRitis ratio and alkaline phosphatase on the prediction of portal vein tumor thrombosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 16;14(1):21614. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72291-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39284840 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization plus stent placement for hepatocellular carcinoma with main portal vein tumor thrombosis: A meta-analysis.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Mar 24;15(3):447-455. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i3.447. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38576592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pirisi M, Avellini C, Fabris C, Scott C, Bardus P, Soardo G, Beltrami CA, Bartoli E. Portal vein thrombosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: age and sex distribution in an autopsy study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1998;124:397–400. - PubMed
-
- Ikai I, Hatano E, Hasegawa S, Fujii H, Taura K, Uyama N, Shimahara Y. Prognostic index for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma combined with tumor thrombosis in the major portal vein. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202:431–438. - PubMed
-
- Wu CC, Hsieh SR, Chen JT, Ho WL, Lin MC, Yeh DC, Liu TJ, P’eng FK. An appraisal of liver and portal vein resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi extending to portal bifurcation. Arch Surg. 2000;135:1273–1279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

