Noradrenaline Modulates the Membrane Potential and Holding Current of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons via β1-Adrenergic Receptors and HCN Channels
- PMID: 29209170
- PMCID: PMC5701640
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00341
Noradrenaline Modulates the Membrane Potential and Holding Current of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons via β1-Adrenergic Receptors and HCN Channels
Abstract
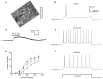
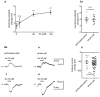
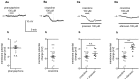
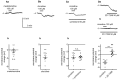
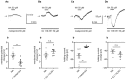
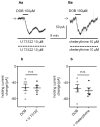
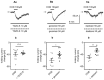
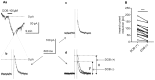
The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) receives dense noradrenergic projections from the locus coeruleus. Adrenergic innervation of mPFC pyramidal neurons plays an essential role in both physiology (control of memory formation, attention, working memory, and cognitive behavior) and pathophysiology (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, cognitive deterioration after traumatic brain injury, behavioral changes related to addiction, Alzheimer's disease and depression). The aim of this study was to elucidate the mechanism responsible for adrenergic receptor-mediated control of the resting membrane potential in layer V mPFC pyramidal neurons. The membrane potential or holding current of synaptically isolated layer V mPFC pyramidal neurons was recorded in perforated-patch and classical whole-cell configurations in slices from young rats. Application of noradrenaline (NA), a neurotransmitter with affinity for all types of adrenergic receptors, evoked depolarization or inward current in the tested neurons irrespective of whether the recordings were performed in the perforated-patch or classical whole-cell configuration. The effect of noradrenaline depended on β1- and not α1- or α2-adrenergic receptor stimulation. Activation of β1-adrenergic receptors led to an increase in inward Na+ current through hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels, which carry a mixed Na+/K+ current. The protein kinase A- and C-, glycogen synthase kinase-3β- and tyrosine kinase-linked signaling pathways were not involved in the signal transduction between β1-adrenergic receptors and HCN channels. The transduction system operated in a membrane-delimited fashion and involved the βγ subunit of G-protein. Thus, noradrenaline controls the resting membrane potential and holding current in mPFC pyramidal neurons through β1-adrenergic receptors, which in turn activate HCN channels via a signaling pathway involving the βγ subunit.
Keywords: HCN channel; adrenergic receptors; holding current; membrane potential; prefrontal cortex; pyramidal neurons; rats; βγ subunit.
Figures




Similar articles
-
alpha2-Noradrenergic receptors activation enhances excitability and synaptic integration in rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons via inhibition of HCN currents.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 15;584(Pt 2):437-50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141671. Epub 2007 Aug 16. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17702809 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Neuropathy Induces HCN Channel Dysfunction in Pyramidal Neurons of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 23;35(38):13244-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0799-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26400952 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic receptor control of pyramidal neuron membrane potential in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in rats.Neuroscience. 2015 Sep 10;303:474-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.023. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26186898
-
Neurophysiology of HCN channels: from cellular functions to multiple regulations.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24184323 Review.
-
β1-adrenoceptor expression on GABAergic interneurons in primate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: potential role in stress-induced cognitive dysfunction.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Mar 15;30:100628. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100628. eCollection 2024 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38550854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paternal methamphetamine exposure induces higher sensitivity to methamphetamine in male offspring through driving ADRB1 on CaMKII-positive neurons in mPFC.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 19;13(1):324. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02624-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37857642 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenergic agonist induces rhythmic firing in quiescent cardiac preganglionic neurons in nucleus ambiguous via activation of intrinsic membrane excitability.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Apr 1;121(4):1266-1278. doi: 10.1152/jn.00761.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 30. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30699052 Free PMC article.
-
β-adrenergic modulation of discrimination learning and memory in the auditory cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Oct;50(7):3141-3163. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14480. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31162753 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomically and functionally distinct locus coeruleus efferents mediate opposing effects on anxiety-like behavior.Neurobiol Stress. 2020 Dec 5;13:100284. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2020.100284. eCollection 2020 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2020. PMID: 33344735 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic signaling mediates cortical early tagging and storage of remote memory.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 9;13(1):7623. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35342-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36494350 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

