The Role of Netrin-1 in Improving Functional Recovery through Autophagy Stimulation Following Spinal Cord Injury in Rats
- PMID: 29209172
- PMCID: PMC5701630
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00350
The Role of Netrin-1 in Improving Functional Recovery through Autophagy Stimulation Following Spinal Cord Injury in Rats
Abstract
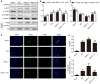
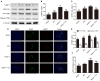
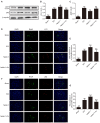
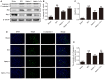
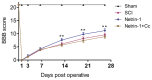
Our previous findings indicated that treatment with Netrin-1 could improve functional recovery through the stimulation of autophagy, by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin (AMPK/mTOR) signaling pathway in rats following spinal cord injury (SCI). However, the underlying mechanisms were not elucidated. The purpose of this study was to investigate the underlying mechanisms by which Netrin-1 promotes autophagy and improves functional recovery after SCI. Following controlled SCI in Sprague-Dawley rats, we observed that the autophagic flux in neurons was impaired, as reflected by the accumulation of light chain 3-II (LC3-II)-positive and LC3-positive autophagosomes (APs), accompanied by the accumulation of the autophagic substrate, Sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1; also known as p62). Our results showed that treatment with Netrin-1 increases the levels of the lysosomal protease cathepsin D (CTSD) and lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1), through the regulation of the nuclear localization of Transcription factor EB (TFEB) via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. In addition, this enhancement of lysosomal biogenesis correlated strongly with the restoration of autophagic flux, inhibition of neural apoptosis and improved functional recovery. Suppression of lysosomal biogenesis via the inhibition of the nuclear translocation of TFEB by Compound C abolished this restoration of autophagic flux and the functional recovery effects of Netrin-1 following SCI. Taken together, these results indicate that Netrin-1 enhances lysosomal biogenesis by regulating the nuclear translocation of TFEB via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Furthermore, the enhancement of lysosomal biogenesis by Netrin-1 following SCI promotes autophagic flux and improves functional recovery in rats. Thus, the regulation of lysosomal biogenesis by modulating the nuclear localization of TFEB might be a novel approach for the treatment of SCI.
Keywords: AMPK; Netrin-1; apoptosis; autophagic flux; mTOR; spinal cord injury; transcription factor EB.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

