Differential Effects of Inhibitor Combinations on Lysophosphatidic Acid-Mediated Chemokine Secretion in Unprimed and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Primed Synovial Fibroblasts
- PMID: 29209219
- PMCID: PMC5702485
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00848
Differential Effects of Inhibitor Combinations on Lysophosphatidic Acid-Mediated Chemokine Secretion in Unprimed and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Primed Synovial Fibroblasts
Abstract
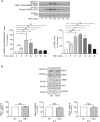
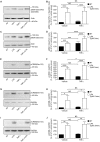
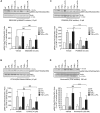
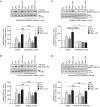
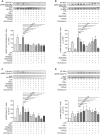
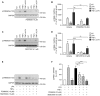
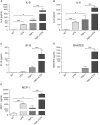
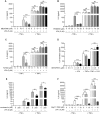
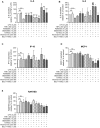
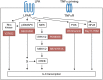
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a pleiotropic bioactive lysophospholipid involved in inflammatory mediator synthesis. Signaling through p38MAPK, ERK, Rho kinase, and MSK-CREB contributes to LPA-mediated IL-8 production in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. The study was undertaken to investigate how LPA activates MSKs and how signaling crosstalk between TNFα and LPA contributes to the super-production of cytokines/chemokines. RAFLS pretreated or not with TNFα were stimulated with LPA. Immunoblotting with phospho-antibodies monitored MSK activation. Cytokine/chemokine production was measured using ELISA and multiplex immunoassays. LPA induced MSK activation by signaling through ERK whereas p38MAPK, Rho kinase, NF-κB or PI3K contribute to IL-8 synthesis mainly via MSK-independent pathways. Priming with TNFα enhanced LPA-mediated MSK phosphorylation and cytokine/chemokine production. After priming with TNFα, inhibition of ERK or MSK failed to attenuate LPA-mediated IL-8 synthesis even if the MSK-CREB signaling axis was completely or partially inhibited. In TNFα-primed cells, inhibition of LPA-mediated cytokine/chemokine synthesis required a specific combination of inhibitors such as p38MAPK and ERK for IL-8 and IL-6, and Rho kinase and NF-κB for MCP-1. The ability of the signaling inhibitors to block LPA induced cytokine/chemokine synthesis is dependent on the inflammatory cytokinic environment. In TNFα-primed RAFLS the super-production of IL-8 and IL-6 induced by LPA occurs mainly via MSK-independent pathways, and simultaneous inhibition of at least two MAPK signaling pathways was required to block their synthesis. Since simultaneous inhibition of both the p38MAPK and ERK-MSK-CREB pathways are required to significantly reduce LPA-mediated IL-8 and IL-6 production in TNFα-preconditioned RAFLS, drug combinations targeting these two pathways are potential new strategies to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Keywords: CREB Fibroblast-like synoviocytes; ERK; MSK; lysophosphatidic acid; p38MAPK; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures
References
-
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., et al. (1988). The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 31 315–324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

