Changes in White-Matter Connectivity in Late Second Language Learners: Evidence from Diffusion Tensor Imaging
- PMID: 29209263
- PMCID: PMC5702476
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02040
Changes in White-Matter Connectivity in Late Second Language Learners: Evidence from Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Abstract
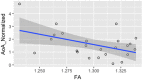
Morphological brain changes as a consequence of new learning have been widely established. Learning a second language (L2) is one such experience that can lead to rapid structural neural changes. However, still relatively little is known about how levels of proficiency in the L2 and the age at which the L2 is learned influence brain neuroplasticity. The goal of this study is to provide novel evidence for the effect of bilingualism on white matter structure in relatively proficient but late L2 learners who acquired the second language after early childhood. Overall, the results demonstrate a significant effect on white matter fractional anisotropy (FA) as a function of L2 learning. Higher FA values were found in a broad white matter network including the anterior thalamic radiation (ATR), the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF), the Uncinate Fasciculus (UF), and the inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF). Moreover, FA values were correlated with age of L2 acquisition, suggesting that learning an L2, even past childhood, induces neural changes. Finally, these results provide some initial evidence that variability in the age of L2 acquisition has important consequences for neural plasticity.
Keywords: age of acquisition; bilingualism; diffusion tensor imaging; neuroplasticity; second language learning.
Figures


References
-
- Abutalebi J., Brambati S. M., Annoni J.-M., Moro A., Cappa S. F., Perani D. (2007). The neural cost of the auditory perception of language switches: an event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging study in bilinguals. J. Neurosci. 27, 13762–13769. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3294-07.2007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abutalebi J., Canini M., Della Rosa P. A., Green D. W., Weekes B. S. (2015a). The neuroprotective effects of bilingualism upon the inferior parietal lobule: a structural neuroimaging study in aging Chinese bilinguals. J. Neurolinguist. 33, 3–13. 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2014.09.008 - DOI
-
- Abutalebi J., Cappa S. F., Perani D. (2001). The bilingual brain as revealed by functional neuroimaging. Bilingual. Lang. Cogn. 4, 179–190. 10.1017/S136672890100027X - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

