The Antifungal Plant Defensin HsAFP1 Is a Phosphatidic Acid-Interacting Peptide Inducing Membrane Permeabilization
- PMID: 29209301
- PMCID: PMC5702387
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02295
The Antifungal Plant Defensin HsAFP1 Is a Phosphatidic Acid-Interacting Peptide Inducing Membrane Permeabilization
Abstract
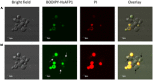
HsAFP1, a plant defensin isolated from coral bells (Heuchera sanguinea), is characterized by broad-spectrum antifungal activity. Previous studies indicated that HsAFP1 binds to specific fungal membrane components, which had hitherto not been identified, and induces mitochondrial dysfunction and cell membrane permeabilization. In this study, we show that HsAFP1 reversibly interacts with the membrane phospholipid phosphatidic acid (PA), which is a precursor for the biosynthesis of other phospholipids, and to a lesser extent with various phosphatidyl inositol phosphates (PtdInsP's). Moreover, via reverse ELISA assays we identified two basic amino acids in HsAFP1, namely histidine at position 32 and arginine at position 52, as well as the phosphate group in PA as important features enabling this interaction. Using a HsAFP1 variant, lacking both amino acids (HsAFP1[H32A][R52A]), we showed that, as compared to the native peptide, the ability of this variant to bind to PA and PtdInsP's is reduced (≥74%) and the antifungal activity of the variant is reduced (≥2-fold), highlighting the link between PA/PtdInsP binding and antifungal activity. Using fluorescently labelled HsAFP1 in confocal microscopy and flow cytometry assays, we showed that HsAFP1 accumulates at the cell surface of yeast cells with intact membranes, most notably at the buds and septa. The resulting HsAFP1-induced membrane permeabilization is likely to occur after HsAFP1's internalization. These data provide novel mechanistic insights in the mode of action of the HsAFP1 plant defensin.
Keywords: antifungal mode of action; lipid membrane target; membrane permeabilization; peptide internalization; plant defensins; yeast.
Figures






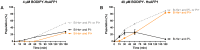
References
-
- Aerts A. M., Francois I. E., Meert E. M., Li Q. T., Cammue B. P., Thevissen K. (2007). The antifungal activity of RsAFP2, a plant defensin from raphanus sativus, involves the induction of reactive oxygen species in Candida albicans. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13 243–247. 10.1159/000104753 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baxter A. A., Richter V., Lay F. T., Poon I. K., Adda C. G., Veneer P. K., et al. (2015). The tomato defensin TPP3 binds phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate via a conserved dimeric cationic grip conformation to mediate cell lysis. Mol. Cell Biol. 35 1964–1978. 10.1128/MCB.00282-15 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

