Diagnosis and treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities and trunk
- PMID: 29209518
- PMCID: PMC5702952
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.170005
Diagnosis and treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities and trunk
Abstract
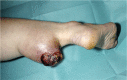
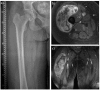
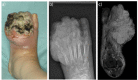
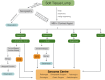
The relatively low incidence and often atypical clinical presentation of soft-tissue sarcomas (STS) impedes early and adequate diagnosis. Patients may report on recently enlarged soft-tissue swellings, infrequently complain of painful lesions, or even have no symptoms at all.A thorough diagnostic work-up is essential in order to distinguish between benign soft-tissue tumours and STSs. Patient history, clinical features and radiological findings all help in assessing the underlying pathology. 'Worrying' features such as recent increase in size, deep location relative to the fascia, a tumour exceeding 4 cm in size, and invasive growth patterns seen on imaging should prompt verification by biopsy.Even though acquisition of biopsy material may be incomplete, one should bear in mind some essential rules. Regardless of the biopsy technique applied, the most direct route to the lump in question should be identified, contamination of adjacent structures should be avoided and a sufficient amount of tissue acquired.Treatment of STS is best planned by a multidisciplinary team, involving experts from various medical specialities. The benchmark therapy consists of en bloc resection of the tumour, covered by a safety margin of healthy tissue. Depending on tumour histology, grade, local extent and anatomical stage, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and isolated hyperthermic limb perfusion may be employed.Due to the complexity of treatment, any soft-tissue swelling suspected of malignancy is best referred directly to a sarcoma centre, where therapeutic management is carefully planned by an experienced multidisciplinary team. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2017;2:421-431. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.170005.
Keywords: diagnostic pathway; soft-tissue sarcoma; therapeutic management.
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: Dr Leithner has recieved grants from Johnson & Johnson, Alphamed and Medtronic, activity outside the submitted work.
Figures
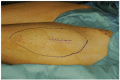
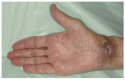
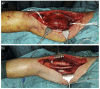
References
-
- Casali PG, Blay JY, ESMO/CONTICANET/EUROBONET Consensus Panel of experts. Soft tissue sarcomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2010;21:v198-v203. - PubMed
-
- Mandahl N. Soft tissue tumors: Lipoma/benign lipomatous tumors. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol 2000;4:135-137.
-
- Wibmer C, Leithner A, Zielonke N, Sperl M, Windhager R. Increasing incidence rates of soft tissue sarcomas? A population-based epidemiologic study and literature review. Ann Oncol 2010;21:1106-1111. - PubMed
-
- Clark MA, Thomas JM. Delay in referral to a specialist soft-tissue sarcoma unit. Eur J Surg Oncol 2005;31:443-448. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

