Final results of the large-scale multinational trial PROFILE 1005: efficacy and safety of crizotinib in previously treated patients with advanced/metastatic ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29209525
- PMCID: PMC5703388
- DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000219
Final results of the large-scale multinational trial PROFILE 1005: efficacy and safety of crizotinib in previously treated patients with advanced/metastatic ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Crizotinib is a potent, orally administered tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We report final results from PROFILE 1005, the largest clinical trial to date for an ALK inhibitor in ALK-positive NSCLC.
Patients and methods: PROFILE 1005 (NCT00932451) was a multicenter, single-arm phase 2 trial of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of crizotinib (250 mg twice daily; 3 week continuous treatment cycles) in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC after failure of ≥1 lines of systemic treatment for locally advanced/metastatic disease. Patients' tumour ALK status was initially determined by a central laboratory until a protocol amendment permitted enrolment of patients based on locally determined ALK status. Co-primary endpoints were objective response rate (ORR), evaluated using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours V.1.1 and adverse events (AEs). Cancer-specific patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were also assessed using the European Organisation for the Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30 and its lung cancer module QLQ-LC13.
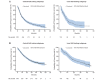
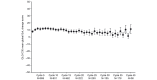
Results: 1069 patients were enrolled; 1066 received crizotinib. The as-treated population comprised 908 and 158 patients, in whom tumour positive ALK-status was determined centrally (± locally) or locally only, respectively. At baseline, a majority of patients were <65 years (84%), 66% were never smokers and 46% were Asian. Derived investigator-assessed ORR was 54% (95% CI 51 to 57) and 41% (95% CI 33 to 49) in the central-testing and local-testing subgroups, respectively. The most common treatment-related AEs in the overall population (any grade) were vision disorder (58%), nausea (51%), diarrhoea (47%) and vomiting (47%). PRO scores demonstrated clinically meaningful improvement in lung cancer symptoms and global quality of life.
Conclusion: The efficacy, safety and PRO profiles of crizotinib in this cohort of 1066 patients with ALK-positive NSCLC are consistent with previous reports.
Trial registration number: Phase 2 trial (NCT00932451); Results.
Keywords: Alk; clinical trial; crizotinib; profile 1005.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: We have already uploaded ICMJE form of each authors when Ann Oncol submission
Figures
References
-
- Kim DW, Ahn M-J, Shi Y, et al. , 2012. Results of a global phase II study with crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive non-small cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) (Poster), American Society of clinical oncology (ASCO) 48th Annual Meeting, Chicago Abstract 7533.
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

