Perturbation of Wound Healing, Cytoskeletal Organization and Cellular Protein Networks during Hazara Virus Infection
- PMID: 29209610
- PMCID: PMC5702460
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00098
Perturbation of Wound Healing, Cytoskeletal Organization and Cellular Protein Networks during Hazara Virus Infection
Abstract
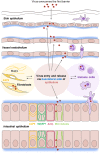
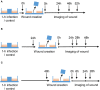
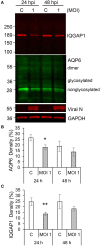
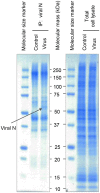
Normal epithelial and endothelial renewal and healing after bacterial and viral challenges are essential for homeostasis along the intestine and the blood and lymphatic vessels. We thus investigated whether and how virus affects migration of human epithelial cells and specifically how the nucleocapsid protein (N) modulates the cellular proteome and interactome using human Caco-2 cells in a wound-healing assay with Hazara virus as a model. Here, Hazara virus blocked cell migration in a dose- and time-dependent manner, disrupted the actin cytoskeleton and specifically reduced the expression of the IQ-motif-containing GTPase-activating protein 1 (IQGAP1) and water channel aquaporin 6 (AQP6) that regulate cytoskeletal organization, water homeostasis and vesicle communication. Moreover, in the Caco-2 cell proteome, we identified several distinct groups of molecules associating with N upon Hazara virus infection, being involved in the ensemble of important cellular processes, e.g., chaperone activity, metabolism, cellular defense against infections, cell morphology, and migration. These events do not only facilitate the virus life cycle, but they are also crucial for membrane and cytoskeleton dynamics, cellular self-renewal and wound healing, being so essential for body integrity and homeostasis.
Keywords: IQGAP1; aquaporin 6; cellular proteome; epithelial barrier; epithelial migration; homeostasis; virus infection.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

