Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced LOX-1+ CD15+ polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29211299
- PMCID: PMC5904716
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12876
Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced LOX-1+ CD15+ polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
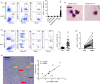
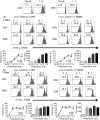
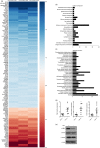
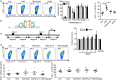
A recent study indicated that Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1) was a distinct surface marker for human polymorphisms myeloid-derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSC). The present study was aimed to investigate the existence LOX-1 PMN-MDSC in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. One hundred and twenty-seven HCC patients, 10 patients with mild active chronic hepatitis B, 10 liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis B, 10 liver dysplastic node with hepatitis B and 50 health control were included. LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSC were significantly elevated in HCC patients compared with healthy control and patients with benign diseases. LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSC in circulation were positively associated with those in HCC tissues. LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSCs significantly reduced proliferation and IFN-γ production of T cells with a dosage dependent manner with LOX-1- CD15+ PMNs reached negative results. The suppression on T cell proliferation and IFN-γ production was reversed by ROS inhibitor and Arginase inhibitor. ROS level and activity of arginase of LOX-1 + CD15+ PMN were higher in LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSCs than LOX-1- CD15+ PMNs, as well as the expression of the NADPH oxidase NOX2 and arginase I. RNA sequence revealed that LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSCs displayed significantly higher expression of spliced X-box -binding protein 1 (sXBP1), an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress marker. ER stress inducer induced LOX-1 expression and suppressive function for CD15+ PMN from health donor. For HCC patients, LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSCs were positively related to overall survival. Above all, LOX-1+ CD15+ PMN-MDSC were elevated in HCC patients and suppressed T cell proliferation through ROS/Arg I pathway induced by ER stress. They presented positive association with the prognosis of HCC patients.
Keywords: endoplasmic reticulum stress; hepatocelluar carcinoma patients; lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor-1; polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cell; prognosis.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Hu CE, Gan J, Zhang RD, Cheng YR, Huang GJ. Up‐regulated myeloid‐derived suppressor cell contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma development by impairing dendritic cell function. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011; 46:156–64. - PubMed
-
- Chiu DK, Xu IM, Lai RK, Tse AP, Wei LL, Koh HY et al Hypoxia induces myeloid‐derived suppressor cell recruitment to hepatocellular carcinoma through chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 26. Hepatology 2016; 64:797–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

