RNAscope in situ hybridization confirms mRNA integrity in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cancer tissue samples
- PMID: 29212158
- PMCID: PMC5706804
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21851
RNAscope in situ hybridization confirms mRNA integrity in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cancer tissue samples
Abstract
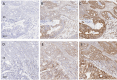
Immunohistochemistry remains the overwhelming technique of choice for test biomarker evaluation in both clinical or research settings when using formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue sections. However, validations can be complex with significant issues about specificity, sensitivity and reproducibility. The vast array of commercially available antibodies from many vendors may also lead to non-standard approaches which are difficult to cross-reference. In contrast mRNA detection, by in situ hybridization (ISH) with sequence specific probes, offers a realistic alternative, with less validation steps and more stringent and reproducible assessment criteria. In the present study mRNA ISH was evaluated in prospectively and retrospectively collected FFPE samples within a cancer biobank setting. Three positive control probes, POLR2A, PPIB and UBC were applied to FFPE sections from a range of tumour types in FFPE whole-face (prospective collection) or TMA (retrospective collection) formats and evaluated semi-quantitatively and by image analysis. Results indicate that mRNA can be robustly evaluated by ISH in prospectively and retrospectively collected tissue samples. Furthermore, for 2 important test biomarkers, PD-L1 and c-MET, we show that mRNA ISH is a technology that can be applied with confidence in the majority of tissue samples because there are quantifiable levels of control probes indicating overall mRNA integrity.
Keywords: FFPE; Integrity; Pathology Section; in situ hybridization; mRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Schalper KA, Velcheti V, Carvajal D, Wimberly H, Brown J, Pusztai L, Rimm DL. In situ tumor PD-L1 mRNA expression is associated with increased TILs and better outcome in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:2773–82. - PubMed
-
- Lewis C, McQuaid S, Hamilton PW, Salto-Tellez M, McArt D, James JA. Building a ‘Repository of Science’: the importance of integrating biobanks within molecular pathology programmes. Eur J Cancer. 2016;67:191–99. - PubMed
-
- Bingham V, Ong CW, James J, Maxwell P, Waugh D, Salto-Tellez M, McQuaid S. PTEN mRNA detection by chromogenic, RNA in situ technologies: a reliable alternative to PTEN immunohistochemistry. Hum Pathol. 2016;47:95–103. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

