Effect of butorphanol, midazolam or ketamine on romifidine based sedation in horses during standing cheek tooth removal
- PMID: 29212478
- PMCID: PMC5719754
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-017-1299-6
Effect of butorphanol, midazolam or ketamine on romifidine based sedation in horses during standing cheek tooth removal
Abstract
Background: Standing surgery, especially dental procedures, are commonly performed in horses. This leads to an increasing demand for reliable sedation protocols. Therefore, it was the purpose of this study to investigate the influence of butorphanol, midazolam or ketamine on romifidine based sedation in horses during cheek tooth removal.
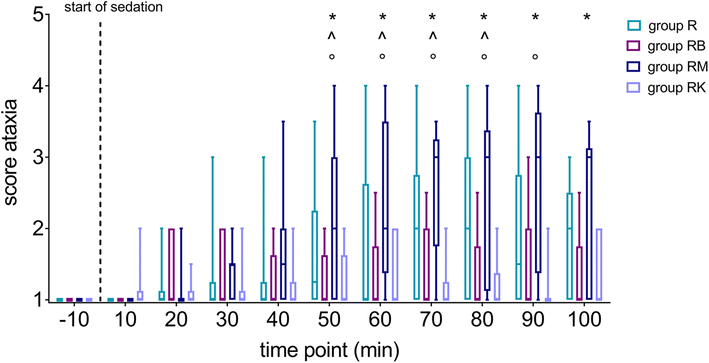
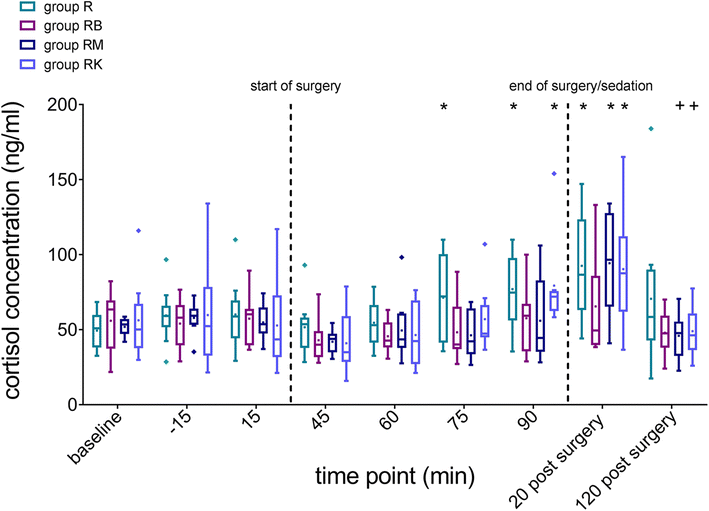
Methods: Forty horses presented for tooth extraction were divided in four groups using matched pair randomization. Group R was sedated with romifidine (bolus 0.03 mg/kg, followed by a constant rate infusion (CRI) 0.05 mg/kg/h) and group RB with romifidine (same dose) and butorphanol (0.02 mg/kg; CRI 0.04 mg/kg/h). Group RM received romifidine (same dose) and midazolam (0.02 mg/kg; CRI 0.06 mg/kg/h) whereas group RK was administered romifidine (same dose) and ketamine (0.5 mg/kg; CRI 1.2 mg/kg/h). If sedation was not adequate a top up bolus of romifidine (0.01 mg/kg) was administered. The quality of sedation and the conditions for tooth extraction, the level of ataxia, chewing, head and tongue movement were evaluated by using a scoring system. The investigator was blinded to the applied sedation protocol. Furthermore, serum cortisol concentrations before, during and after the procedure were analyzed to gain more information about the stress level of the horses.
Results: Horses in group RM showed significantly less chewing and tongue activity compared to horses sedated with romifidine alone or with butorphanol additionally, but also significantly higher levels of ataxia. The quality of sedation was significantly better if romifidine was administered in combination with ketamine compared to romifidine alone. Furthermore, horses of group RK needed less additional romifidine boli compared to all other groups. Blood cortisol concentrations during surgery in groups RB and RM remained unchanged. Horses of group R showed higher cortisol concentrations during sedation compared to horses of groups RB and RM.
Conclusion: Romifidine alone at an initial bolus dose of 0.03 mg/kg followed by a constant rate infusion of 0.05 mg/kg/h was insufficient to obtain an adequate level of sedation and led to increased stress levels, whereas the addition of butorphanol inhibited the stress response. The combination of romifidine with either midazolam or ketamine improved sedation quality and surgical conditions.
Keywords: Cheek tooth removal; Horse; Ketamine; Midazolam; Romifidine; Sedation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
The protocol was reviewed and approved by an internal, institutional committee (University of Veterinary Medicine, Hannover). The protocol was also approved by the “Animal Welfare Committee” of the University of Veterinary Medicine, Hannover University. In our case this committee not only decided that the study protocol met all necessary requirements but also concluded that the study design met all requirements of good and common clinical practice regardless of the assignment to a specific group in this study. Therefore, step three, approval by the state committee, the “Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments of Lower Saxony” Germany, was not necessary for this specific study.
Before conducting the sedation and dental procedure all owners were informed about this study and gave their consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of a romifidine constant rate infusion with or without butorphanol for standing sedation of horses.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2012 Jan;39(1):12-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2011.00681.x. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22151873 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of a romifidine constant rate infusion protocol with or without butorphanol for dentistry and ophthalmologic procedures in standing horses.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2014 Sep;41(5):491-7. doi: 10.1111/vaa.12174. Epub 2014 May 17. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24835127 Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a xylazine constant rate infusion with or without butorphanol for standing sedation of horses.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2012 Jan;39(1):1-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2011.00653.x. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 22103355 Clinical Trial.
-
Avian Sedation.J Avian Med Surg. 2021 Sep;35(3):253-268. doi: 10.1647/20-00045. J Avian Med Surg. 2021. PMID: 34677024 Review.
-
How to score sedation and adjust the administration rate of sedatives in horses: a literature review and introduction of the Ghent Sedation Algorithm.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2019 Jan;46(1):4-13. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2019. PMID: 30528671 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical effect of buprenorphine or butorphanol, in combination with detomidine and diazepam, on sedation and postoperative pain after cheek tooth extraction in horses.Can Vet J. 2022 Jan;63(1):39-46. Can Vet J. 2022. PMID: 34975166 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Butorphanol, Buprenorphine and Levomethadone on Sedation Quality and Postoperative Analgesia in Horses Undergoing Cheek Tooth Extraction.Vet Sci. 2022 Apr 6;9(4):174. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9040174. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35448672 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of dexmedetomidine with midazolam for dental surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22288. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022288. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120732 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiorespiratory, Sedative and Antinociceptive Effects of a Medetomidine Constant Rate Infusion with Morphine, Ketamine or Both.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jul 13;11(7):2081. doi: 10.3390/ani11072081. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359209 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Detomidine or Romifidine in Combination with Morphine for Standing Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Horses.Vet Sci. 2024 Mar 8;11(3):124. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11030124. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38535858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeRossi R, Jorge TP, Ossuna MR, Carneiro RPB, Alves OD, Zanenga NF. Sedation and pain management with intravenous Romifidine−Butorphanol in standing horses. J Equine Vet Sci. 2009;29(2):75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2008.12.004. - DOI
-
- Ringer SK, Schwarzwald CC, Portier KG, Ritter A, Bettschart-Wolfensberger R. Effects on cardiopulmonary function and oxygen delivery of doses of romifidine and xylazine followed by constant rate infusions in standing horses. Vet J. 2013;195(2):228–234. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2012.06.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Sanroman FJ, Holmbak-Petersen R, Varela M, del Alamo AM, Santiago I. Accelerometric comparison of the locomotor pattern of horses sedated with xylazine hydrochloride, detomidine hydrochloride, or romifidine hydrochloride. Am J Vet Res. 2013;74(6):828–834. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.74.6.828. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

