Identification of the lipid biomarkers from plasma in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by Lipidomics
- PMID: 29212488
- PMCID: PMC5719761
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-017-0513-4
Identification of the lipid biomarkers from plasma in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by Lipidomics
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an irreversible interstitial pulmonary disease featured by high mortality, chronic and progressive course, and poor prognosis with unclear etiology. Currently, more studies have been focusing on identifying biomarkers to predict the progression of IPF, such as genes, proteins, and lipids. Lipids comprise diverse classes of molecules and play a critical role in cellular energy storage, structure, and signaling. The role of lipids in respiratory diseases, including cystic fibrosis, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has been investigated intensely in the recent years. The human serum lipid profiles in IPF patients however, have not been thoroughly understood and it will be very helpful if there are available molecular biomarkers, which can be used to monitor the disease progression or provide prognostic information for IPF disease.
Methods: In this study, we performed the ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF/MS) to detect the lipid variation and identify biomarker in plasma of IPF patients. The plasma were from 22 IPF patients before received treatment and 18 controls.
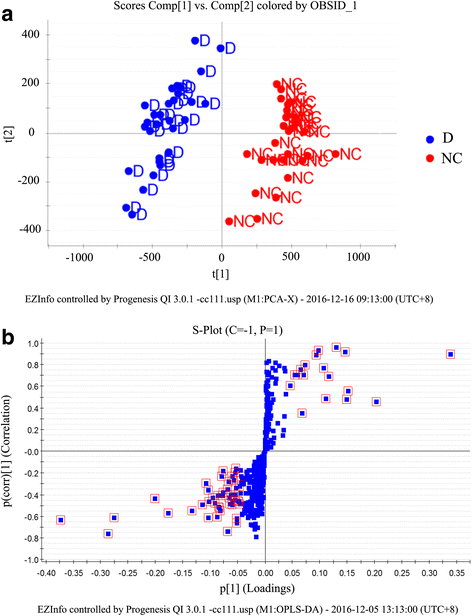
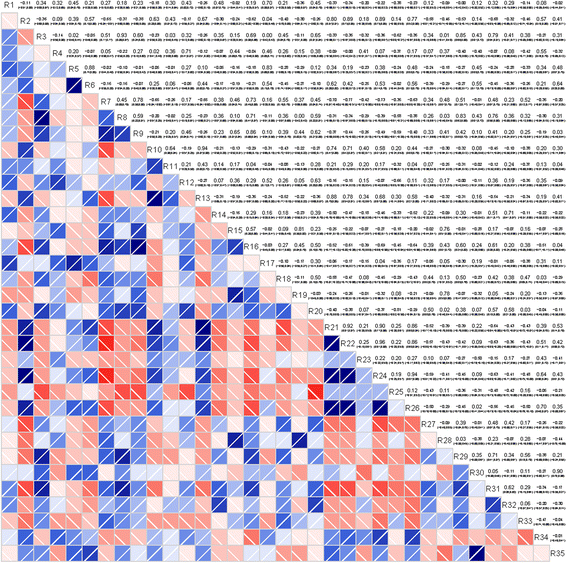
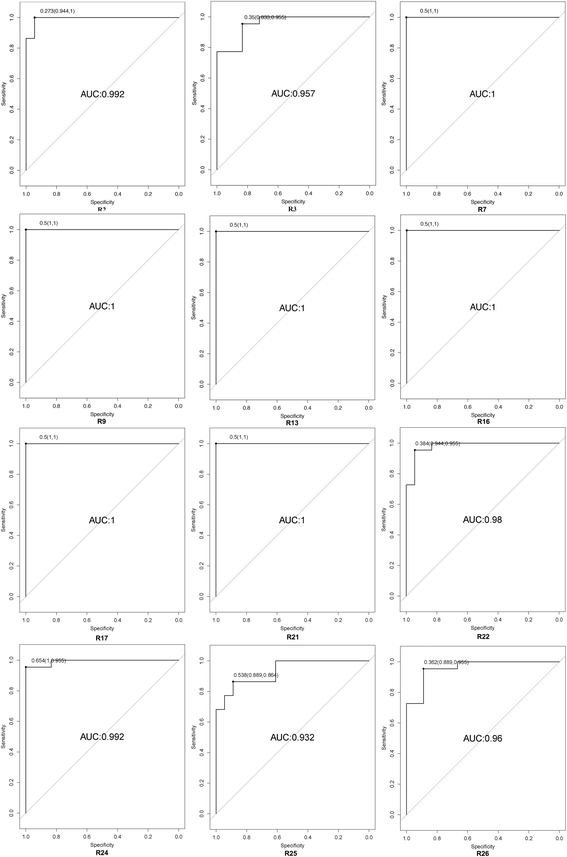
Results: A total of 507 individual blood lipid species were determined with lipidomics from the 40 plasma samples including 20 types of fatty acid, 159 types of glycerolipids, 221 types of glycerophospholipids, 47 types of sphingolipids, 46 types of sterol lipids, 7 types of prenol lipids, 3 types of saccharolipids, and 4 types of polyketides. By comparing the variations in the lipid metabolite levels in IPF patients, a total of 62 unique lipids were identified by statistical analysis including 24 kinds of glycerophoslipids, 30 kinds of glycerolipids, 3 kinds of sterol lipids, 4 kinds of sphingolipids and 1 kind of fatty acids. Finally, 6 out of 62 discriminating lipids were selected as the potential biomarkers, which are able to differentiate between IPF disease and controls with ROC analysis.
Conclusions: Our results provided vital information regarding lipid metabolism in IPF patients and more importantly, a few potentially promising biomarkers were firstly identified which may have a predictive role in monitoring and diagnosing IPF disease.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Lipid; Lipidomics; Plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The clinical IPF samples included in this study were collected from the First hospital of Tsinghua University. All patient data were anonymous, so informed consent for participation was not required. The use of these samples was approved by the Institutional Review Board for human studies at the First Hospital of Tsinghua University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
There is detectable variation in the lipidomic profile between stable and progressive patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).Respir Res. 2021 Apr 9;22(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01682-3. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33836757 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted metabolomics of human plasma reveal lipid markers unique to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021 May;15(2-3):e2000039. doi: 10.1002/prca.202000039. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021. PMID: 33580915
-
The potential lipid biomarker 5-HETE for acute exacerbation identified by metabolomics in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respirology. 2025 Feb;30(2):158-167. doi: 10.1111/resp.14866. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Respirology. 2025. PMID: 39681341
-
Lipid metabolism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to therapy.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Aug;101(8):905-915. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02336-1. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37289208 Review.
-
Blood Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Lung. 2017 Jun;195(3):273-280. doi: 10.1007/s00408-017-9993-5. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Lung. 2017. PMID: 28353114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipids in Equine Airway Inflammation: An Overview of Current Knowledge.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;14(12):1812. doi: 10.3390/ani14121812. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Analysis of Targeted Serum Lipidomics in Patients with Pneumoconiosis - China, 2022.China CDC Wkly. 2023 Sep 22;5(38):849-855. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2023.161. China CDC Wkly. 2023. PMID: 37814648 Free PMC article.
-
The causal relationship between genetically predicted blood metabolites and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 16;19(4):e0300423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300423. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38626141 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of HMGCS2 mediated AECIIs lipid metabolic alteration promotes pulmonary fibrosis by activating fibroblasts.Respir Res. 2024 Apr 24;25(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02816-z. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38658970 Free PMC article.
-
Blood lipid profiles as a prognostic biomarker in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2024 Jul 18;25(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02905-z. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39026259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chuchalin AG. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ter Arkh. 2000;72(3):5–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

