Hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 29212549
- PMCID: PMC5719571
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0625-0
Hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis
Abstract
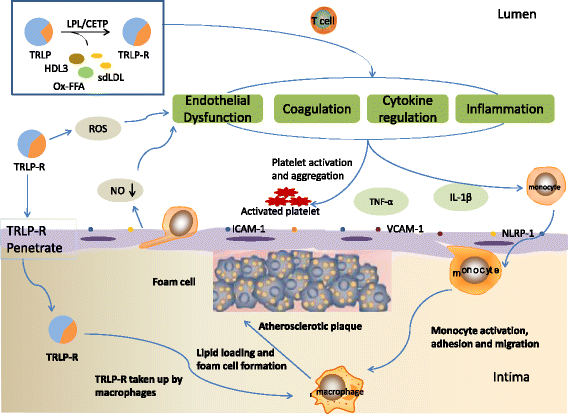
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is the leading cause of death and it has been confirmed that increased low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis. Recently, the increasing evidence has showed that hypertriglyceridemia is associated with incremental ASCVD risk. But the proatherogenic mechanism of triglyceride (TG) remains unclear. Therefore, this article focuses on the clinical studies and proatherogenic mechanism related to hypertriglyceridemia, in order to provide reference for the prevention and treatment of ASCVD.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; Lipoprotein; Triglyceride.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors reported no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Chapman MJ, Ginsberg HN, Amarenco P, Andreotti F, Boren J, Catapano AL, Descamps OS, Fisher E, Kovanen PT, Kuivenhoven JA, et al. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: evidence and guidance for management. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

