Galectin-3 impacts Cryptococcus neoformans infection through direct antifungal effects
- PMID: 29213074
- PMCID: PMC5719036
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02126-7
Galectin-3 impacts Cryptococcus neoformans infection through direct antifungal effects
Abstract
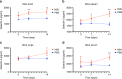
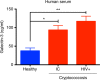
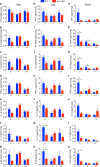
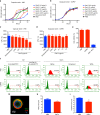
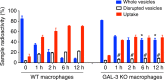
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated fungal pathogen that causes cryptococcosis, which is a major opportunistic infection in immunosuppressed individuals. Mammalian β-galactoside-binding protein Galectin-3 (Gal-3) modulates the host innate and adaptive immunity, and plays significant roles during microbial infections including some fungal diseases. Here we show that this protein plays a role also in C. neoformans infection. We find augmented Gal-3 serum levels in human and experimental infections, as well as in spleen, lung, and brain tissues of infected mice. Gal-3-deficient mice are more susceptible to cryptococcosis than WT animals, as demonstrated by the higher fungal burden and lower animal survival. In vitro experiments show that Gal-3 inhibits fungal growth and exerts a direct lytic effect on C. neoformans extracellular vesicles (EVs). Our results indicate a direct role for Gal-3 in antifungal immunity whereby this molecule affects the outcome of C. neoformans infection by inhibiting fungal growth and reducing EV stability, which in turn could benefit the host.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Heitman J, Kozel TR, Kwon-Chung J, Perfect JR, Casadevall A. Cryptococcus: From Human Pathogen to Model Yeast. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2011.
-
- Lindell DM, Ballinger MN, McDonald RA, Toews GB, Huffnagle GB. Immunologic homeostasis during infection: coexistence of strong pulmonary cell-mediated immunity to secondary Cryptococcus neoformans infection while the primary infection still persists at low levels in the lungs. J. Immunol. 2006;177:4652–4661. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4652. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

