High-quality draft genome sequence of Aquidulcibacter paucihalophilus TH1-2T isolated from cyanobacterial aggregates in a eutrophic lake
- PMID: 29213356
- PMCID: PMC5712168
- DOI: 10.1186/s40793-017-0284-9
High-quality draft genome sequence of Aquidulcibacter paucihalophilus TH1-2T isolated from cyanobacterial aggregates in a eutrophic lake
Abstract
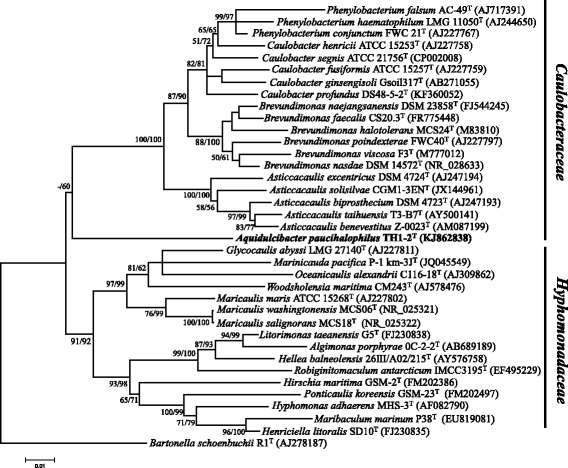
Aquidulcibacter paucihalophilus TH1-2T is a member of the family Caulobacteraceae within Alphaproteobacteria isolated from cyanobacterial aggregates in a eutrophic lake. The draft genome comprises 3,711,627 bp and 3489 predicted protein-coding genes. The genome of strain TH1-2T has 270 genes encoding peptidases. And metallo and serine peptidases were found most frequently. A high number of genes encoding carbohydrate active enzymes (141 CAZymes) also present in strain TH1-2T genome. Among CAZymes, 47 glycoside hydrolase families, 37 glycosyl transferase families, 38 carbohydrate esterases families, nine auxiliary activities families, seven carbohydrate-binding modules families, and three polysaccharide lyases families were identified. Accordingly, strain TH1-2T has a high number of transporters (91), the dominated ones are ATP-binding cassette transporters (61) and TonB-dependent transporters (28). Major TBDTs are Group I, which consisted of transporters for various types of dissolved organic matter. These genome features indicate adaption to cyanobacterial aggregates microenvironments.
Keywords: Aquidulcibacter paucihalophilus; Carbohydrate active enzyme; Cyanobacterial aggregates; Peptidase; Transporter.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Wang H, Lu J, Wang W, Yang L, Chen Y. Methane fluxes from the littoral zone of hypereutrophic Taihu Lake, China. J Geophys Res. 2006;111:D17109. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006864. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

