Calcium Dysregulation in Alzheimer's Disease: A Target for New Drug Development
- PMID: 29214114
- PMCID: PMC5713908
- DOI: 10.4172/2161-0460.1000374
Calcium Dysregulation in Alzheimer's Disease: A Target for New Drug Development
Abstract
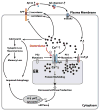
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disorder and the most common cause of dementia among aged people whose population is rapidly increasing. AD not only seriously affects the patient's physical health and quality of life, but also adds a heavy burden to the patient's family and society. It is urgent to understand AD pathogenesis and develop the means of prevention and treatment. AD is a chronic devastating neurodegenerative disease without effective treatment. Current approaches for management focus on helping patients relieve or delay the symptoms of cognitive dysfunction. The calcium ion (Ca2+) is an important second messenger in the function and structure of nerve cell circuits in the brain such as neuronal growth, exocytosis, as well as in synaptic and cognitive function. Increasing numbers of studies suggested that disruption of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis, especially the abnormal and excessive Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via the ryanodine receptor (RYR), plays important roles in orchestrating the dynamic of the neuropathology of AD and associated memory loss, cognitive dysfunction. Dantrolene, a known antagonist of the RYR and a clinically available drug to treat malignant hyperthermia, can ameliorate the abnormal Ca2+ release from the RYR in AD and the subsequent pathogenesis, such as increased β-secretase and γ-secretase activities, production of Amyloid-β 42 (Aβ 42) and its oligomer, impaired autophagy, synapse dysfunction, and memory loss. However, more studies are needed to confirm the efficacy and safety repurposing dantrolene as a therapeutic drug in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Calcium; Dantrolene; Ryanodine receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dantrolene : From Malignant Hyperthermia to Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(9):668-676. doi: 10.2174/1871527317666180619162649. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 29921212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein mishandling and impaired lysosomal proteolysis generated through calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 6;119(49):e2211999119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2211999119. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36442130 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches to Optimizing Dantrolene Neuroprotection for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2020;17(4):324-328. doi: 10.2174/1567205017666200522204722. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2020. PMID: 32442084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Ca2+ homeostasis dysregulation in Alzheimer's disease: a focus on plasma membrane and cell organelles.FASEB J. 2019 Jun;33(6):6697-6712. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801751R. Epub 2019 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30848934 Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal Dantrolene as a Disease-Modifying Drug in Alzheimer 5XFAD Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;76(4):1375-1389. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200227. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32623395 Free PMC article.
-
Memory and Learning Deficits Are Associated With Ca2+ Dyshomeostasis in Normal Aging.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jul 16;12:224. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00224. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32765253 Free PMC article.
-
Novel early-onset Alzheimer-associated genes influence risk through dysregulation of glutamate, immune activation, and intracell signaling pathways.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 5:rs.3.rs-4480585. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4480585/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jun;21(6):e70377. doi: 10.1002/alz.70377. PMID: 38883718 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Pruritus and Neuropsychiatric Symptoms Among Patients with Darier Disease-An Overlooked and Interconnected Challenge.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 8;14(6):1818. doi: 10.3390/jcm14061818. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142630 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Treatment of Wolfram Syndrome.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 27;19(5):2755. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19052755. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35270448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12:459–509. - PubMed
-
- Cummings JL, Victoroff JI. Noncognitive neuropsychiatric syndromes in Alzheimer’s disease. Cogn Behav Neurol. 1990;3:140–158.
-
- Association A. 2017 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13:325–373.
-
- Sherman MA, Lesné SE. Detecting aβ* 56 oligomers in brain tissues. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;670:45–56. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous