A Novel and Selective Nociceptin Receptor (NOP) Agonist (1-(1-((cis)-4-isopropylcyclohexyl)piperidin-4-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl)methanol (AT-312) Decreases Acquisition of Ethanol-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Mice
- PMID: 29215139
- PMCID: PMC5785446
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13575
A Novel and Selective Nociceptin Receptor (NOP) Agonist (1-(1-((cis)-4-isopropylcyclohexyl)piperidin-4-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl)methanol (AT-312) Decreases Acquisition of Ethanol-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Mice
Abstract
Background: Nociceptin/orphanin FQ, the endogenous peptide agonist for the opioid receptor-like receptor (also known as NOP or the nociceptin receptor), has been shown to block the acquisition and expression of ethanol (EtOH)-induced conditioned place preference (CPP). Here, we report the characterization of a novel small-molecule NOP ligand AT-312 (1-(1-((cis)-4-isopropylcyclohexyl)piperidin-4-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl)methanol) in receptor binding and GTPγS functional assays in vitro. We then investigated the effect of AT-312 on the rewarding action of EtOH in mice using the CPP paradigm. Further, using mice lacking the NOP receptor and their wild-type controls, we also examined the involvement of NOP in the effect of AT-312. Motivational effects of AT-312 alone were also assessed in the CPP paradigm.
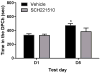
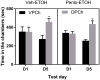
Methods: Female mice lacking NOP and/or their wild-type controls received conditioning in the presence or absence of the NOP agonist [AT-312 (1, 3, and 10 mg/kg) or the control NOP agonist SCH221510 (10 mg/kg)] followed by saline/EtOH for 3 consecutive days (twice daily) and tested for CPP in a drug-free state on the next day.
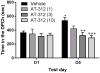
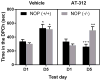
Results: Our in vitro data showed that AT-312 is a high-affinity, selective NOP full agonist with 17-fold selectivity over the mu opioid receptor and >200-fold selectivity over the kappa opioid receptor. The results of our in vivo studies showed that AT-312 reduced EtOH CPP at the lowest dose (1 mg/kg) tested but completely abolished EtOH CPP at higher doses (3 or 10 mg/kg) compared to their vehicle-treated control group. AT-312 (3 mg/kg) did not alter EtOH-induced CPP in mice lacking NOP, confirming that AT-312 reduced EtOH CPP through its action at the NOP receptor. AT-312 (3 mg/kg) did not induce reward or aversion when administered alone, showing that the novel small-molecule NOP agonist shows efficacy in blocking EtOH-induced CPP via the NOP receptor.
Conclusions: Together, these data suggest that small-molecule NOP agonists have the potential to reduce alcohol reward and may be promising as medications to treat alcohol addiction.
Keywords: AT-312; Alcohol Reward; Ethanol-Induced Conditioned Place Preference; NOP Agonist; NOP Knockout Mouse.
Copyright © 2017 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. NTZ, WEP and MEM are employees of Astraea Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Altshuler HL, Phillips PE, Feinhandler DA. Alteration of ethanol self-administration by naltrexone. Life Sci. 1980;26:679–688. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin D, Grant ER, Pohorecky LA. Naltrexone reverses ethanol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in awake, freely moving rats. Brain Res. 1993;621:137–140. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y-C, Prusoff WH. Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973;22:3099–3108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

