Improved EGFR mutation detection using combined exosomal RNA and circulating tumor DNA in NSCLC patient plasma
- PMID: 29216356
- PMCID: PMC5889041
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdx765
Improved EGFR mutation detection using combined exosomal RNA and circulating tumor DNA in NSCLC patient plasma
Abstract
Background: A major limitation of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) for somatic mutation detection has been the low level of ctDNA found in a subset of cancer patients. We investigated whether using a combined isolation of exosomal RNA (exoRNA) and cell-free DNA (cfDNA) could improve blood-based liquid biopsy for EGFR mutation detection in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Patients and methods: Matched pretreatment tumor and plasma were collected from 84 patients enrolled in TIGER-X (NCT01526928), a phase 1/2 study of rociletinib in mutant EGFR NSCLC patients. The combined isolated exoRNA and cfDNA (exoNA) was analyzed blinded for mutations using a targeted next-generation sequencing panel (EXO1000) and compared with existing data from the same samples using analysis of ctDNA by BEAMing.
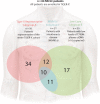
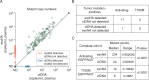
Results: For exoNA, the sensitivity was 98% for detection of activating EGFR mutations and 90% for EGFR T790M. The corresponding sensitivities for ctDNA by BEAMing were 82% for activating mutations and 84% for T790M. In a subgroup of patients with intrathoracic metastatic disease (M0/M1a; n = 21), the sensitivity increased from 26% to 74% for activating mutations (P = 0.003) and from 19% to 31% for T790M (P = 0.5) when using exoNA for detection.
Conclusions: Combining exoRNA and ctDNA increased the sensitivity for EGFR mutation detection in plasma, with the largest improvement seen in the subgroup of M0/M1a disease patients known to have low levels of ctDNA and poses challenges for mutation detection on ctDNA alone.
Clinical trials: NCT01526928.
Figures
Comment in
-
Combining plasma-based biosources to predict treatment response in NSCLC patients.Ann Oncol. 2018 Sep 1;29(9):2022. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy246. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30010765 No abstract available.
-
Improved EGFR mutation detection using combined exosomal RNA and circulating tumor DNA in NSCLC patient plasma.Ann Oncol. 2018 Oct 1;29(10):2143. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy261. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30060089 No abstract available.
-
Combined exosomal RNA and circulating tumor DNA for epidermal growth factor mutation detection in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Nov;10(Suppl 33):S4023-S4027. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.17. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30631545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gadgeel SM. Personalized therapy of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adv Exp Med Biol 2016; 890: 203–222. - PubMed
-
- Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T. et al. Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (INTEREST): a randomised phase III trial. Lancet 2008; 372(9652): 1809–1818. - PubMed
-
- Brock G, Castellanos-Rizaldos E, Hu L. et al. Liquid biopsy for cancer screening, patient stratification and monitoring. Transl Cancer Res 2015; 3: 280–290.
-
- Reckamp KL, Melnikova VO, Karlovich C. et al. A highly sensitive and quantitative test platform for detection of NSCLC EGFR mutations in urine and plasma. J Thorac Oncol 2016; 11(10): 1690–1700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

