Differences in Prevalence of Symptomatic Zika Virus Infection, by Age and Sex-Puerto Rico, 2016
- PMID: 29216376
- PMCID: PMC8849542
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jix630
Differences in Prevalence of Symptomatic Zika Virus Infection, by Age and Sex-Puerto Rico, 2016
Abstract
Background: During the outbreak of Zika virus (ZIKV) disease in Puerto Rico in 2016, nonpregnant women aged 20-39 years were disproportionately identified with ZIKV disease. We used household-based cluster investigations to determine whether this disparity was associated with age- or sex-dependent differences in the rate of ZIKV infection or reported symptoms.
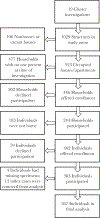
Methods: Participation was offered to residents of households within a 100-m radius of the residences of a convenience sample of 19 laboratory-confirmed ZIKV disease cases. Participants answered a questionnaire and provided specimens for diagnostic testing by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results: Among 367 study participants, 114 (31.1%) were laboratory positive for ZIKV infection, of whom 30% reported a recent illness (defined as self-reported rash or arthralgia) attributable to ZIKV infection. Age and sex were not associated with ZIKV infection. Female sex (adjusted prevalence ratio [aPR], 2.28; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.40, 3.67), age <40 years (aPR, 2.39; 95% CI, 1.55, 3.70), and asthma (aPR, 1.63; 95% CI, 1.12, 2.37) were independently associated with symptomatic infection.
Conclusions: Although neither female sex nor age were associated with an increased prevalence of ZIKV infection, both were associated with symptomatic infection. Further investigation to identify a potential mechanism of age- and sex-dependent differences in reporting symptomatic ZIKV infection is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Age and Sex in the Zika Pandemic Era.J Infect Dis. 2018 May 5;217(11):1675-1677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix631. J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29216367 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pan American Health Organization. Zika Epidemiological Update, 17 November. Washington, D.C.: Pan American Health Organization / World Health Organization, 2016.
-
- Duffy MR, Chen TH, Hancock WT, et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N Engl J Med 2009; 360:2536–43. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Zika Strategic Response Plan, Revised for July 2016 - December 2017. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

