Age-Dependent Effects of apoE Reduction Using Antisense Oligonucleotides in a Model of β-amyloidosis
- PMID: 29216448
- PMCID: PMC5728673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.014
Age-Dependent Effects of apoE Reduction Using Antisense Oligonucleotides in a Model of β-amyloidosis
Abstract
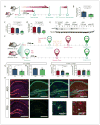
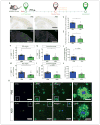
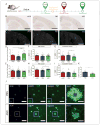
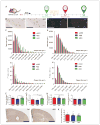
The apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer disease. Previous studies suggest that reduction of apoE levels through genetic manipulation can reduce Aβ pathology. However, it is not clear how reduction of apoE levels after birth would affect amyloid deposition. We utilize an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) to reduce apoE expression in the brains of APP/PS1-21 mice homozygous for the APOE-ε4 or APOE-ε3 allele. ASO treatment starting after birth led to a significant decrease in Aβ pathology when assessed at 4 months. Interestingly, ASO treatment starting at the onset of amyloid deposition led to an increase in Aβ plaque size and a reduction in plaque-associated neuritic dystrophy with no change in overall plaque load. These results suggest that lowering apoE levels prior to plaque deposition can strongly affect the initiation of Aβ pathology while lowering apoE after Aβ seeding modulates plaque size and toxicity.
Keywords: APOE; ASO; Alzheimer disease; Aβ; amyloid-β; antisense oligonucleotides; apolipoprotein E.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Seeds of Destruction: New Mechanistic Insights into the Role of Apolipoprotein E4 in Alzheimer's Disease.Neuron. 2017 Dec 6;96(5):953-955. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.022. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 29216455
References
-
- Bennett CF, Swayze EE. RNA targeting therapeutics: molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology. 2010;50:259–293. - PubMed
-
- Bero AW, Bauer AQ, Stewart FR, White BR, Cirrito JR, Raichle ME, Culver JP, Holtzman DM. Bidirectional relationship between functional connectivity and amyloid-beta deposition in mouse brain. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2012;32:4334–4340. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE. Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nature genetics. 2007;39:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Bien-Ly N, Gillespie AK, Walker D, Yoon SY, Huang Y. Reducing human apolipoprotein E levels attenuates age-dependent Abeta accumulation in mutant human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2012;32:4803–4811. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

