Refugees' experiences of healthcare in the host country: a scoping review
- PMID: 29216876
- PMCID: PMC5721651
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-017-2731-0
Refugees' experiences of healthcare in the host country: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: During the last years, Europe experienced an increase in immigration due to a variety of worldwide wars and conflicts, which in turn resulted in a greater number of physical and mental health issues present among the refugees. These factors place high demands not only on the refugees, but also on healthcare professionals who meet the refugees in different situations. Information about the refugees' experiences of the healthcare systems in their host countries is urgently needed to improve the quality of healthcare delivered, as well as to provide opportunities for better access. The aim of this scoping review is to compile research about the experiences that the refugees have with the healthcare systems in their host countries.
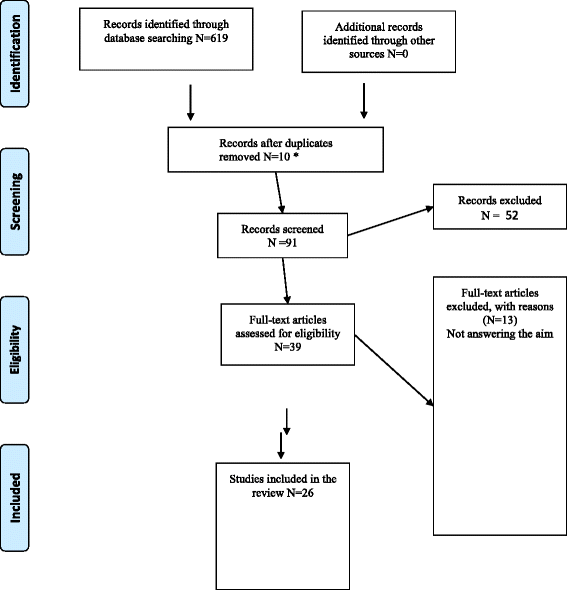
Methods: This study was conducted as a scoping review and the methodology is derived from Levac et al. and with inspiration from the framework of Arksey & O'Malley. A systematic article search was done in Medline, Cinahl and Psychinfo. A total of 619 articles were found in the search and finally 26 articles met the inclusion criteria and were included.
Results: The results show that communication between healthcare professionals and refugees is important, however, insufficient language knowledge acts as an effective communication barrier. There is a need for more information to be given to the refugees about the reception country's healthcare system in both oral and written formats, as well as the right to healthcare. Support from healthcare professionals is also important for refugees to have a positive experience with healthcare. In some of the studies included, refugees experienced discrimination due to low proficiency in the language of the host country, and/or because of their race or accent, which shows that culturally appropriate healthcare is needed for them.
Conclusions: Since refugees are suffering from poor mental and physical health and could therefore be at a greater risk of morbidity and mortality in comparison to the rest of the population of the host country, there is an urgent need for improvements in communication, interpretation, support, and deliverance of culturally appropriate healthcare.
Keywords: Communication; Experiences; Healthcare; Refugees; Scoping review; Support.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
EM works as senior lecturer/postdoc researcher at Malmö University, department of Care Science. KSF is working as a senior lecturer/postdoc researcher at Malmö University, department of Care Science.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
-
- WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health, World Health Organization . Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through action on the social determinants of health: commission on social determinants of health final report: World Health Organization. 2008.
-
- Björngren Cuadra C, Carlzén K. Anonymous Malmö Institute for Studies of migration, diversity and welfare (MIM), Malmö University. 2015. Inledning MILSA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous