Changes in salivary oxytocin after inhalation of clary sage essential oil scent in term-pregnant women: a feasibility pilot study
- PMID: 29216912
- PMCID: PMC5721455
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-017-3053-3
Changes in salivary oxytocin after inhalation of clary sage essential oil scent in term-pregnant women: a feasibility pilot study
Abstract
Objectives: This pilot study using a quasi-experimental design was conducted to evaluate the feasibility (i.e., limited efficacy, practicality, and acceptability) of our intervention protocol involving inhalation of the scent of clary sage essential oil by pregnant women and measurement of their preinhalation and postinhalation oxytocin levels.
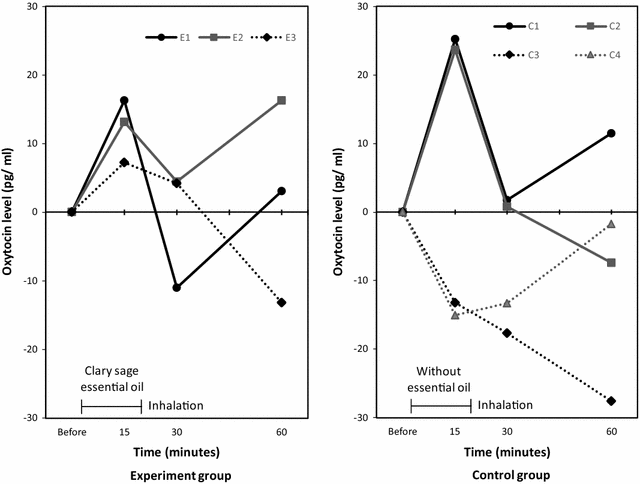
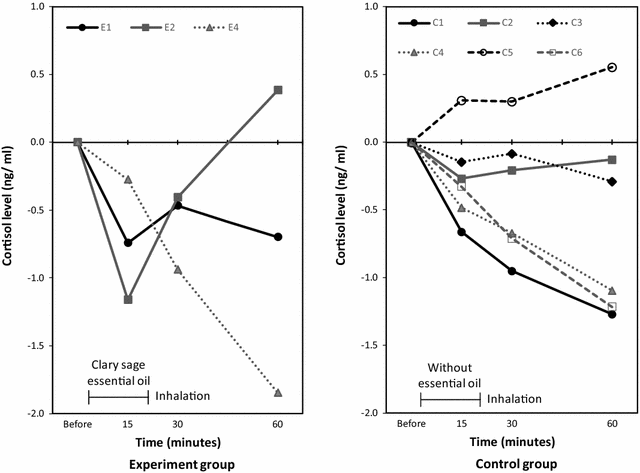
Results: Participants were women of singleton pregnancies between 38 and 40 gestation weeks (N = 11). The experiment group (n = 5) inhaled the scent of clary sage essential oil diluted 50-fold with 10 mL of odorless propylene glycol for 20 min. Regarding limited efficacy, the oxytocin level 15 min postinhalation increased in 3 women and was unmeasurable in 2. The control group (n = 6) inhaled similarly without the 50-fold dilution of clary sage essential oil. Their oxytocin level increased in 2 women, decreased in 2, and was unmeasurable in 2. Uterine contraction was not observed in both groups. Regarding practicality, 3 of the 11 women could not collect sufficient saliva. The cortisol level decreased in both groups postinhalation. The protocol had no negative effects. Regarding acceptability, burden of the protocol was not observed. Trial registration The Clinical Trials Registry of University Hospital Medical Information Network in Japan-UMIN000017830. Registered: June 8, 2015.
Keywords: Aromatherapy; Clary sage essential oil; Complementary and alternative medicine; Feasibility study; Induction of labor; Inhalation; Pregnant women; Salivary cortisol; Salivary oxytocin; Uterine contraction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in Salivary Oxytocin Level of Term Pregnant Women after Aromatherapy Footbath for Spontaneous Labor Onset: A Non-Randomized Experimental Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jun 30;20(13):6262. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20136262. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37444109 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Essential Oil on Salivary Oxytocin Concentration in Postmenopausal Women.J Altern Complement Med. 2020 Mar;26(3):226-230. doi: 10.1089/acm.2019.0361. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Altern Complement Med. 2020. PMID: 32013535
-
Changes in 5-hydroxytryptamine and cortisol plasma levels in menopausal women after inhalation of clary sage oil.Phytother Res. 2014 Nov;28(11):1599-605. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5163. Epub 2014 May 7. Phytother Res. 2014. PMID: 24802524
-
Effects of breast stimulation for spontaneous onset of labor on salivary oxytocin levels in low-risk pregnant women: A feasibility study.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 15;13(2):e0192757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192757. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29447299 Free PMC article.
-
Intraplantar injection of bergamot essential oil into the mouse hindpaw: effects on capsaicin-induced nociceptive behaviors.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;85:237-48. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(09)85018-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19607974 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Salivary Oxytocin Level of Term Pregnant Women after Aromatherapy Footbath for Spontaneous Labor Onset: A Non-Randomized Experimental Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jun 30;20(13):6262. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20136262. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37444109 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women during interaction with an infant: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Feb 24;21(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-03609-8. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 33627086 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility Study for a Randomized Controlled Trial of Aromatherapy Footbath for Stimulating Onset of Labor in Term Pregnant Women.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jun 17;22(6):950. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22060950. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40566376 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oxytocin levels in low-risk primiparas following breast stimulation for spontaneous onset of labor: a quasi-experimental study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019 Oct 12;19(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2504-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019. PMID: 31604456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osterman MJK, Martin JA. Data brief 155: recent declines in induction of labor by gestational age. NCHS Data Brief. 2014;155:1–8. - PubMed
-
- American College of Nurse-Midwives. Midwives Alliance of North America. National Association of Certified Professional Midwives Supporting healthy and normal physiologic childbirth: a consensus statement by the American College of Nurse-Midwives, Midwives Alliance of North America, and the National Association of Certified Professional Midwives. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2012;57:529–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-2011.2012.00218.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

