Structure of the human TRPM4 ion channel in a lipid nanodisc
- PMID: 29217581
- PMCID: PMC5898196
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aar4510
Structure of the human TRPM4 ion channel in a lipid nanodisc
Abstract
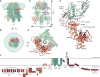
Transient receptor potential (TRP) melastatin 4 (TRPM4) is a widely expressed cation channel associated with a variety of cardiovascular disorders. TRPM4 is activated by increased intracellular calcium in a voltage-dependent manner but, unlike many other TRP channels, is permeable to monovalent cations only. Here we present two structures of full-length human TRPM4 embedded in lipid nanodiscs at ~3-angstrom resolution, as determined by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. These structures, with and without calcium bound, reveal a general architecture for this major subfamily of TRP channels and a well-defined calcium-binding site within the intracellular side of the S1-S4 domain. The structures correspond to two distinct closed states. Calcium binding induces conformational changes that likely prime the channel for voltage-dependent opening.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
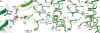
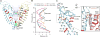
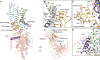
Comment in
-
TRPM channels come into focus.Science. 2018 Jan 12;359(6372):160-161. doi: 10.1126/science.aar6205. Science. 2018. PMID: 29326261 No abstract available.
References
-
- Julius D. TRP channels and pain. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2013;29:355–384. - PubMed
-
- Launay P, et al. TRPM4 is a Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channel mediating cell membrane depolarization. Cell. 2002;109:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Launay P, et al. TRPM4 regulates calcium oscillations after T cell activation. Science. 2004;306:1374–1377. - PubMed
-
- Nilius B, et al. Voltage dependence of the Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:30813–30820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

