Different mutational rates and mechanisms in human cells at pregastrulation and neurogenesis
- PMID: 29217587
- PMCID: PMC6311130
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aan8690
Different mutational rates and mechanisms in human cells at pregastrulation and neurogenesis
Abstract
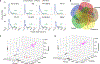
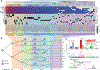
Somatic mosaicism in the human brain may alter function of individual neurons. We analyzed genomes of single cells from the forebrains of three human fetuses (15 to 21 weeks postconception) using clonal cell populations. We detected 200 to 400 single-nucleotide variations (SNVs) per cell. SNV patterns resembled those found in cancer cell genomes, indicating a role of background mutagenesis in cancer. SNVs with a frequency of >2% in brain were also present in the spleen, revealing a pregastrulation origin. We reconstructed cell lineages for the first five postzygotic cleavages and calculated a mutation rate of ~1.3 mutations per division per cell. Later in development, during neurogenesis, the mutation spectrum shifted toward oxidative damage, and the mutation rate increased. Both neurogenesis and early embryogenesis exhibit substantially more mutagenesis than adulthood.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
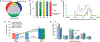

Comment in
-
Tracing single-cell histories.Science. 2018 Feb 2;359(6375):521-522. doi: 10.1126/science.aar6335. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Science. 2018. PMID: 29420280 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

