P2X7 receptor regulates sympathoexcitatory response in myocardial infarction rats via NF-κB and MAPK pathways
- PMID: 29218093
- PMCID: PMC5714779
P2X7 receptor regulates sympathoexcitatory response in myocardial infarction rats via NF-κB and MAPK pathways
Retraction in
-
P2X7 receptor regulates sympathoexcitatory response in myocardial infarction rats via NF-κB and MAPK pathways [Retraction].Am J Transl Res. 2018 Sep 15;10(9):2996. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30323886 Free PMC article.
Abstract
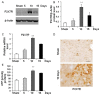
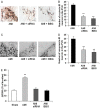
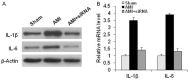
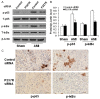
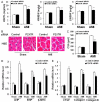
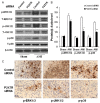
Previous studies have provided evidence for the regulatory effect of P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) on cardiovascular activities. Our study focused on exploring the function and fundamental mechanism of microglial P2X7R in controlling sympathoexcitatory response using rats with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Coronary artery ligation was used in rats to cause AMI. And before that, rats were administrated with P2X7R siRNA that targeted P2X7R mRNA into paraventricular nucleus (PVN) or BBG (Brilliant Blue G, a P2X7 receptor antagonist). Increased expression levels of P2X7R and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) were observed in the hypothalamic PVN of AMI rats. Moreover, the knockdown of P2X7R expression by P2X7-siRNA or suppression of P2X7 receptor by BBG attenuated the elevation of both vasopressin and oxytocin levels in the PVNs of AMI rats. There was also a decrease in renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) by P2X7-siRNA and BBG. Besides, inflammation was alleviated by P2X7-siRNA and BBG through suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 in PVN of AMI rats. Furthermore, blockade of P2X7R moderated the process of cardiac remodeling. This was achieved due to the regulatory effect of P2X7R on sympathoexcitatory response by influencing NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. These findings suggest that P2X7R can act as a new regulator of sympathoexcitatory response via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in AMI rats.
Keywords: AMI; MAPK; NF-κB; P2X7 receptor; PVN; microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Goldberg RJ, Spencer FA, Yarzebski J, Lessard D, Gore JM, Alpert JS, Dalen JE. A 25-year perspective into the changing landscape of patients hospitalized with acute myocardial infarction (the worcester heart attack study) Am J Cardiol. 2004;94:1373–1378. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern SM, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O’Donnell C, Roger V, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wilson M, Hong Y American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2008 update: a report from the American heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117:e25–146. - PubMed
-
- Inoue K. Microglial activation by purines and pyrimidines. Glia. 2002;40:156–163. - PubMed
-
- Parvathenani LK, Tertyshnikova S, Greco CR, Roberts SB, Robertson B, Posmantur R. P2X7 mediates superoxide production in primary microglia and is up-regulated in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13309–13317. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
