Dexmedetomidine alleviates LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in mice
- PMID: 29218102
- PMCID: PMC5714788
Dexmedetomidine alleviates LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in mice
Abstract
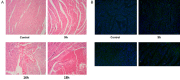
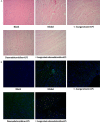
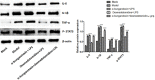
This study was conducted to investigate the role of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy in mice. C57BL/6 mice were used to construct septic cardiomyopathy models. The optimal duration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment was determined by HE staining and TUNEL assay. Blank controls were intraperitoneally injected with saline and models were injected with LPS (10 mg/kg) (LPS), α-bungarotoxin (BT-LPS), BT and dexmedetomidine (BT-DEX-LPS). The pathological examinations were performed on HE- stained myocardium tissues, apoptosis was determined using TUNEL assay, mRNA expression of NF-κB p65, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, Bcl-2, Bax, p53 and α7nACh was quantified using qRT-PCR, protein levels of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3) were analyzed using Western blot analysis. HE staining and TUNEL assays showed that the optimal LPS treatment time for septic cardiomyopathy induction was 16 h. Compared with the blank control, mice in LPS group had significantly higher apoptosis, while DEX and BT reduced apoptosis when they were used separately and increased apoptosis when they were used jointly. In the LPS-treated mice, the levels of NF-κb p65, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, Bax, p53, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and p-STAT3 were significantly increased, while α7nAChR level was decreased significantly (P < 0.01); DEX alone had no impact on the expression of these proteins but significantly up-regulated the expression of these genes except α7nAChR when used jointly with BT (P < 0.01). It is clear that DEX can alleviate heart injury, while α7nAChR-specific blocker BT is antagonistic against the anti-inflammatory effect of DEX on sepsis in mice.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; apoptosis; gene expression; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GTS-21 attenuates LPS-induced renal injury via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in mice.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Oct 15;9(10):4673-4681. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 29118926 Free PMC article.
-
GTS-21 Protected Against LPS-Induced Sepsis Myocardial Injury in Mice Through α7nAChR.Inflammation. 2018 Jun;41(3):1073-1083. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0759-x. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29680908
-
Effect of splenectomy on attenuation of LPS-induced AKI through GTS-21-induced cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Apr 15;11(4):2540-2549. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31105861 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Renal-Splenic Axis Involvement in Acute Kidney Injury Mediated by the α7nAChR-NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2021 Apr;44(2):746-757. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01374-y. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33141376
-
Dexmedetomidine-mediated protection against septic liver injury depends on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling downregulation partly via cholinergic anti-inflammatory mechanisms.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Nov;76:105898. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105898. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31520992
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine-induced cardioprotection is mediated by inhibition of high mobility group box-1 and the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 25;14(7):e0218726. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218726. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31344138 Free PMC article.
-
Circulatory effects of dexmedetomidine in early sepsis: a randomised controlled experimental study.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;393(1):89-97. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01713-3. Epub 2019 Aug 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31422445
-
Circumferential strain rate to detect lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction: a speckle tracking echocardiography study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019 Feb;9(2):151-159. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.11.03. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019. PMID: 30976539 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in vitro by inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome activation.BMC Anesthesiol. 2021 Apr 6;21(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01334-5. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021. PMID: 33823789 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging protective roles of shengmai injection in septic cardiomyopathy in mice by inducing myocardial mitochondrial autophagy via caspase-3/Beclin-1 axis.Inflamm Res. 2020 Jan;69(1):41-50. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01292-2. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Inflamm Res. 2020. Retraction in: Inflamm Res. 2023 Apr;72(4):745. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01706-2. PMID: 31712853 Retracted.
References
-
- Kalil AC, Dakroub H, Freifeld AG. Sepsis and solid organ transplantation. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:533–541. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier J, Luyt CE, Fulla Y, Vinsonneau C, Cariou A, Grabar S, Dhainaut JF, Mira JP, Chiche JD. Brain natriuretic peptide: a marker of myocardial dysfunction and prognosis during severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:660–665. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Huang JL, Zhang YL, Wang CC, Zhou JR, Ma Q, Wang X, Shen XH, Jiang CL. Enhanced phosphorylation of MAPKs by NE promotes TNF-alpha production by macrophage through alpha adrenergic receptor. Inflammation. 2012;35:527–534. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 2002;420:853–859. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
