Cross-sectional associations between sleep duration, sedentary time, physical activity, and adiposity indicators among Canadian preschool-aged children using compositional analyses
- PMID: 29219077
- PMCID: PMC5773862
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4852-0
Cross-sectional associations between sleep duration, sedentary time, physical activity, and adiposity indicators among Canadian preschool-aged children using compositional analyses
Abstract
Background: Sleep duration, sedentary behaviour, and physical activity are three co-dependent behaviours that fall on the movement/non-movement intensity continuum. Compositional data analyses provide an appropriate method for analyzing the association between co-dependent movement behaviour data and health indicators. The objectives of this study were to examine: (1) the combined associations of the composition of time spent in sleep, sedentary behaviour, light-intensity physical activity (LPA), and moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity (MVPA) with adiposity indicators; and (2) the association of the time spent in sleep, sedentary behaviour, LPA, or MVPA with adiposity indicators relative to the time spent in the other behaviours in a representative sample of Canadian preschool-aged children.
Methods: Participants were 552 children aged 3 to 4 years from cycles 2 and 3 of the Canadian Health Measures Survey. Sedentary time, LPA, and MVPA were measured with Actical accelerometers (Philips Respironics, Bend, OR USA), and sleep duration was parental reported. Adiposity indicators included waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI) z-scores based on World Health Organization growth standards. Compositional data analyses were used to examine the cross-sectional associations.
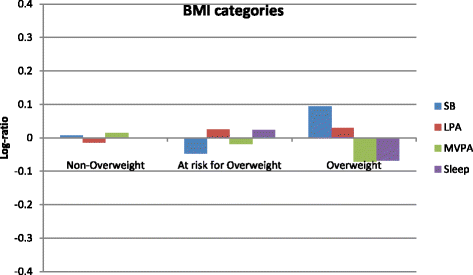
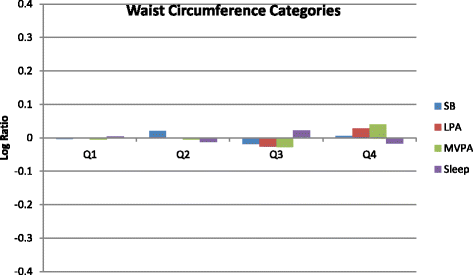
Results: The composition of movement behaviours was significantly associated with BMI z-scores (p = 0.006) but not with WC (p = 0.718). Further, the time spent in sleep (BMI z-score: γ sleep = -0.72; p = 0.138; WC: γ sleep = -1.95; p = 0.285), sedentary behaviour (BMI z-score: γ SB = 0.19; p = 0.624; WC: γ SB = 0.87; p = 0.614), LPA (BMI z-score: γ LPA = 0.62; p = 0.213, WC: γ LPA = 0.23; p = 0.902), or MVPA (BMI z-score: γ MVPA = -0.09; p = 0.733, WC: γ MVPA = 0.08; p = 0.288) relative to the other behaviours was not significantly associated with the adiposity indicators.
Conclusions: This study is the first to use compositional analyses when examining associations of co-dependent sleep duration, sedentary time, and physical activity behaviours with adiposity indicators in preschool-aged children. The overall composition of movement behaviours appears important for healthy BMI z-scores in preschool-aged children. Future research is needed to determine the optimal movement behaviour composition that should be promoted in this age group.
Keywords: Adiposity; Physical activity; Preschool children; Sedentary behaviour; Sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval for the CHMS was obtained from Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada Research Ethics Board. Written informed consent was obtained from a parent or guardian, and assent was obtained from the child.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Chastin SF, Palarea-Albaladejo J, Dontje ML, Skelton DA. Combined effects of time spent in physical activity, sedentary behaviors and sleep on obesity and cardio-metabolic health markers: a novel compositional data analysis approach. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139984. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

