Systematic review of the relationships between sedentary behaviour and health indicators in the early years (0-4 years)
- PMID: 29219092
- PMCID: PMC5773886
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4849-8
Systematic review of the relationships between sedentary behaviour and health indicators in the early years (0-4 years)
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this systematic review was to examine the relationships between sedentary behaviour (SB) and health indicators in children aged 0 to 4 years, and to determine what doses of SB (i.e., duration, patterns [frequency, interruptions], and type) were associated with health indicators.
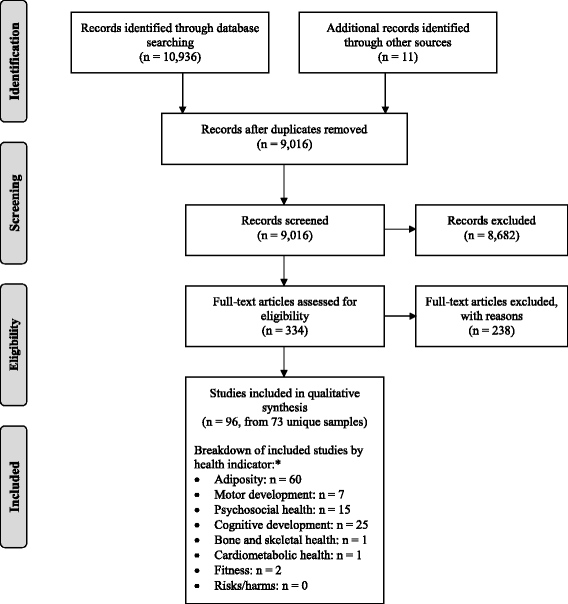
Methods: Online databases were searched for peer-reviewed studies that met the a priori inclusion criteria: population (apparently healthy, 1 month to 4.99 years), intervention/exposure and comparator (durations, patterns, and types of SB), and outcome/health indicator (critical: adiposity, motor development, psychosocial health, cognitive development; important: bone and skeletal health, cardiometabolic health, fitness, risks/harm). The quality of the evidence was assessed by study design and outcome using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) framework.
Results: Due to heterogeneity, meta-analyses were not possible; instead, narrative syntheses were conducted, structured around the health indicator and type of SB. A total of 96 studies were included (195,430 participants from 33 countries). Study designs were: randomized controlled trial (n = 1), case-control (n = 3), longitudinal (n = 25), longitudinal with additional cross-sectional analyses (n = 5), and cross-sectional (n = 62). Evidence quality ranged from "very low" to "moderate". Associations between objectively measured total sedentary time and indicators of adiposity and motor development were predominantly null. Associations between screen time and indicators of adiposity, motor or cognitive development, and psychosocial health were primarily unfavourable or null. Associations between reading/storytelling and indicators of cognitive development were favourable or null. Associations between time spent seated (e.g., in car seats or strollers) or in the supine position, and indicators of adiposity and motor development, were primarily unfavourable or null. Data were scarce for other outcomes.
Conclusions: These findings continue to support the importance of minimizing screen time for disease prevention and health promotion in the early years, but also highlight the potential cognitive benefits of interactive non-screen-based sedentary behaviours such as reading and storytelling. Additional high-quality research using valid and reliable measures is needed to more definitively establish the relationships between durations, patterns, and types of SB and health indicators, and to provide insight into the appropriate dose of SB for optimal health in the early years.
Keywords: Adiposity; Bone and skeletal health; Cardiometabolic health; Cognitive development; Early years; Fitness; Infants; Motor development; Preschoolers; Reading; Risks; Screen time; Sedentary behaviour; Sitting; Toddlers.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous