Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer
- PMID: 29219147
- PMCID: PMC5835768
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2017.155
Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer
Abstract
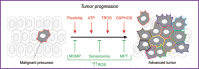
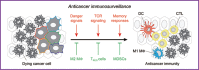
Glycolysis has long been considered as the major metabolic process for energy production and anabolic growth in cancer cells. Although such a view has been instrumental for the development of powerful imaging tools that are still used in the clinics, it is now clear that mitochondria play a key role in oncogenesis. Besides exerting central bioenergetic functions, mitochondria provide indeed building blocks for tumor anabolism, control redox and calcium homeostasis, participate in transcriptional regulation, and govern cell death. Thus, mitochondria constitute promising targets for the development of novel anticancer agents. However, tumors arise, progress, and respond to therapy in the context of an intimate crosstalk with the host immune system, and many immunological functions rely on intact mitochondrial metabolism. Here, we review the cancer cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic mechanisms through which mitochondria influence all steps of oncogenesis, with a focus on the therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondrial metabolism for cancer therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Bui JD, Schreiber RD. Cancer immunosurveillance, immunoediting and inflammation: independent or interdependent processes? Curr Opin Immunol 2007; 19:203–208. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Senovilla L, Galluzzi L, Andre F, Zitvogel L. Natural and therapy-induced immunosurveillance in breast cancer. Nat Med 2015; 21:1128–1138. - PubMed
-
- Erez A, DeBerardinis RJ. Metabolic dysregulation in monogenic disorders and cancer - finding method in madness. Nat Rev Cancer 2015; 15:440–448. - PubMed
-
- Danhier P, Banski P, Payen VL, et al. Cancer metabolism in space and time: beyond the Warburg effect. Biochim Biophys Acta 2017; 1858:556–572. - PubMed
-
- Chen DS, Mellman I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017; 541:321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

