Measurement of full-thickness macular hole size using en face optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 29219961
- PMCID: PMC5848286
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2017.254
Measurement of full-thickness macular hole size using en face optical coherence tomography
Abstract
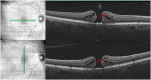
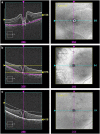
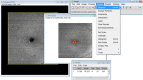
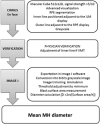
PurposeTo assess the feasibility and interest of measuring macular hole (MH) size using en face optical coherence tomography (OCT) compared with manual diameter measurements on B-scans.MethodsAmong our previously published series of 100 patients operated for primary MH, patients whose images were acquired with Cirrus 5000 HD-OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec) with a quality signal strength >5/10 were included. Three segmentations (internal limiting membrane, horizontal, and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)) were compared for obtaining the most appropriate en face image. MH surface areas were measured using ImageJ software. Mean diameters calculated from surface areas (diameter=2 × √(surface area/π)) were compared with those measured on B-scans.ResultsNineteen patients were included with a mean age of 72±8 years (56-86) and a female predominance (3/16). The mean absolute difference between horizontal and vertical diameters measured on B-scans was of 54±47 μm (0-180) without reaching significance (P=0.874). RPE segmentation provided the best en face image and was feasible without and with adjustment, respectively, in 79% and 100% (cases with vitreomacular traction) of cases. No significant difference in mean diameters was observed between those calculated from en face images (435±143 μm (195-693)) and those measured on horizontal B-scans (426±139 μm (214-705), P=0.482).ConclusionMeasuring MH size on en face OCT images is feasible, reliable, and eliminates the potential bias related to manual measurements on B-scans. Its integration into OCT devices would offer an automated and easy-to-use option for clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gass JD. Reappraisal of biomicroscopic classification of stages of development of a macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol 1995; 119(6): 752–759. - PubMed
-
- Duker JS, Kaiser PK, Binder S, de Smet MD, Gaudric A, Reichel E et al. The International Vitreomacular Traction Study Group classification of vitreomacular adhesion, traction, and macular hole. Ophthalmology 2013; 120(12): 2611–2619. - PubMed
-
- Haller JA, Stalmans P, Benz MS, Gandorfer A, Pakola SJ, Girach A et al. Efficacy of intravitreal ocriplasmin for treatment of vitreomacular adhesion: subgroup analyses from two randomized trials. Ophthalmology 2015; 122(1): 117–122. - PubMed
-
- Ip MS, Baker BJ, Duker JS, Reichel E, Baumal CR, Gangnon R et al. Anatomical outcomes of surgery for idiopathic macular hole as determined by optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 2002; 120(1): 29–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

