Integrating 5hmC and gene expression data to infer regulatory mechanisms
- PMID: 29220513
- PMCID: PMC5925763
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx777
Integrating 5hmC and gene expression data to infer regulatory mechanisms
Abstract
Motivation: Epigenetic mechanisms are known to play a major role in breast cancer. However, the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) remains understudied. We hypothesize that 5hmC mediates redox regulation of gene expression in an aggressive subtype known as triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). To address this, our objective was to highlight genes that may be the target of this process by identifying redox-regulated, antioxidant-sensitive, gene-localized 5hmC changes associated with mRNA changes in TNBC cells.
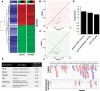
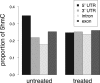
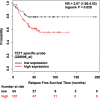
Results: We proceeded to develop an approach to integrate novel Pvu-sequencing and RNA-sequencing data. The result of our approach to merge genome-wide, high-throughput TNBC cell line datasets to identify significant, concordant 5hmC and mRNA changes in response to antioxidant treatment produced a gene set with relevance to cancer stem cell function. Moreover, we have established a method that will be useful for continued research of 5hmC in TNBC cells and tissue samples.
Availability and implementation: Data are available at Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under accession number GSE103850.
Contact: bollig@karmanos.org.
Figures

References
-
- Ahsan S., Drăghici S. (2017) Identifying significantly impacted pathways and putative mechanisms with iPathwayGuide. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 57, 7–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

