Drug treatment of hypertension in Sweden in relation to sex, age, and comorbidity
- PMID: 29220556
- PMCID: PMC8031007
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13149
Drug treatment of hypertension in Sweden in relation to sex, age, and comorbidity
Abstract
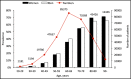
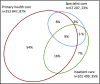
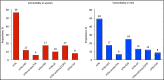
The authors investigated antihypertensive drug treatment in Sweden using the Stockholm Regional Healthcare Data Warehouse, providing information on all healthcare consultations, diagnoses, hospitalizations, dispensed prescription drugs, sex, and age in 2.1 million persons. This cross-sectional analysis identified 292 428 individuals 20 years or older with hypertension (mean age 68 ± 13 years, 53% women). About half had no diabetes mellitus or cardiovascular comorbidity. The number of dispensed drugs was lower in women than in men (1.9 ± 1.3 vs 2.1 ± 1.5, P < .001). Women more often used diuretics, angiotensin receptor blockers, and β-blockers, while men used more angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and calcium channel blockers (all P < .01). In women, 66% with diabetes mellitus and 72% with heart failure used angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers vs 76% and 79% in men (all P < .001, adjusted for age and comorbidity). Thus, sex differences in treatment prevail. There is room for improvement, which could reduce cardiovascular complications.
Keywords: antihypertensive agents; blood pressure; cardiovascular disease; diabetes mellitus; hypertension; primary health care; sex; treatment.
©2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
Antihypertensive drug treatment: the real-life challenge.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018 Jan;20(1):115-117. doi: 10.1111/jch.13147. Epub 2017 Dec 8. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018. PMID: 29220544 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kahan T, Dahlgren H, deFaire U , et al. Moderately elevated blood pressure. A systematic literature review. Stockholm: The Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care 2004–update 2007. Report 170/1U:1–195.
-
- Wolf‐Maier K, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA. 2003;289:2363‐2369. - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747‐1757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

