hnRNPK Recruits PCGF3/5-PRC1 to the Xist RNA B-Repeat to Establish Polycomb-Mediated Chromosomal Silencing
- PMID: 29220657
- PMCID: PMC5735038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.013
hnRNPK Recruits PCGF3/5-PRC1 to the Xist RNA B-Repeat to Establish Polycomb-Mediated Chromosomal Silencing
Abstract
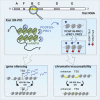
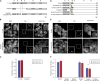
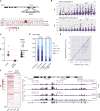
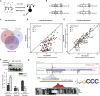
The Polycomb-repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 play a key role in chromosome silencing induced by the non-coding RNA Xist. Polycomb recruitment is initiated by the PCGF3/5-PRC1 complex, which catalyzes chromosome-wide H2A lysine 119 ubiquitylation, signaling recruitment of other PRC1 complexes, and PRC2. However, the molecular mechanism for PCGF3/5-PRC1 recruitment by Xist RNA is not understood. Here we define the Xist RNA Polycomb Interaction Domain (XR-PID), a 600 nt sequence encompassing the Xist B-repeat element. Deletion of XR-PID abolishes Xist-dependent Polycomb recruitment, in turn abrogating Xist-mediated gene silencing and reversing Xist-induced chromatin inaccessibility. We identify the RNA-binding protein hnRNPK as the principal XR-PID binding factor required to recruit PCGF3/5-PRC1. Accordingly, synthetically tethering hnRNPK to Xist RNA lacking XR-PID is sufficient for Xist-dependent Polycomb recruitment. Our findings define a key pathway for Polycomb recruitment by Xist RNA, providing important insights into mechanisms of chromatin modification by non-coding RNA.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PCGF3/5-PRC1 initiates Polycomb recruitment in X chromosome inactivation.Science. 2017 Jun 9;356(6342):1081-1084. doi: 10.1126/science.aal2512. Science. 2017. PMID: 28596365 Free PMC article.
-
Xist Deletional Analysis Reveals an Interdependency between Xist RNA and Polycomb Complexes for Spreading along the Inactive X.Mol Cell. 2019 Apr 4;74(1):101-117.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.015. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30827740 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Xist-mediated Polycomb recruitment in the initiation of X-chromosome inactivation.EMBO Rep. 2019 Oct 4;20(10):e48019. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948019. Epub 2019 Aug 27. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31456285 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb complexes in X chromosome inactivation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;372(1733):20170021. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0021. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28947664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The many faces of Polycomb regulation by RNA.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Apr;61:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.02.023. Epub 2020 May 11. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32403014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of RNA-protein networks with RNP-MaP defines functional hubs on RNA.Nat Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;39(3):347-356. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0709-7. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Nat Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33077962 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-Smad7 mediates cross-talk between Nodal/TGF-β and BMP signaling to regulate cell fate determination of pluripotent and multipotent cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 14;50(18):10526-10543. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac780. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36134711 Free PMC article.
-
PR-DUB safeguards Polycomb repression through H2AK119ub1 restriction.Cell Prolif. 2023 Oct;56(10):e13457. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13457. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36959757 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile functions of RNA m6A machinery on chromatin.J Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Jul 8;14(3):mjac011. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac011. J Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35212732 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy between Variant PRC1 Complexes Defines Polycomb-Mediated Gene Repression.Mol Cell. 2019 Jun 6;74(5):1020-1036.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.024. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31029541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arrigoni R., Alam S.L., Wamstad J.A., Bardwell V.J., Sundquist W.I., Schreiber-Agus N. The Polycomb-associated protein Rybp is a ubiquitin binding protein. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:6233–6241. - PubMed
-
- Beard C., Hochedlinger K., Plath K., Wutz A., Jaenisch R. Efficient method to generate single-copy transgenic mice by site-specific integration in embryonic stem cells. Genesis. 2006;44:23–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

