Nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk prediction via salivary detection of host and Epstein-Barr virus genetic variants
- PMID: 29221111
- PMCID: PMC5707005
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11144
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk prediction via salivary detection of host and Epstein-Barr virus genetic variants
Abstract
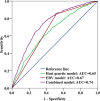
Genetic susceptibility and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection are important etiological factors in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). In this study, in southern China, where NPC is endemic, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the EBV-encoded RPMS1 gene (locus 155391: G > A [G155391A]) and seven host SNPs (rs1412829, rs28421666, rs2860580, rs2894207, rs31489, rs6774494, and rs9510787) were confirmed to be significantly associated with NPC risk in 50 NPC cases versus 54 hospital-based controls with throat washing specimens and 1925 NPC cases versus 1947 hospital-based controls with buffy coat samples, respectively. We established a strategy to detect the NPC-associated EBV and host SNPs using saliva samples in a single test that is convenient, noninvasive, and cost-effective and displays good compliance. The potential utility of this strategy was tested by applying a risk prediction model integrating these EBV and host genetic variants to a population-based case-control study comprising 1026 incident NPC cases and 1148 controls. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis revealed an area under the curve of the NPC risk prediction model of 0.74 (95% CI: 0.71-0.76). Net reclassification improvement (NRI) analysis showed that inclusion of the EBV SNP significantly improved the discrimination ability of the model (NRI = 0.30, P < 0.001), suggesting the promising value of EBV characteristics for identifying high-risk NPC individuals in endemic areas. Taken together, we developed a promising NPC risk prediction model via noninvasive saliva sampling. This approach might serve as a convenient and effective method for screening the population with high-risk of NPC.
Keywords: case-control; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; risk prediction; saliva.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A single nucleotide polymorphism in the Epstein-Barr virus genome is strongly associated with a high risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chin J Cancer. 2015 Dec 16;34(12):563-72. doi: 10.1186/s40880-015-0073-z. Chin J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26675171 Free PMC article.
-
Host genetic variants, Epstein-Barr virus subtypes, and the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Assessment of interaction and mediation.Cell Genom. 2024 Feb 14;4(2):100474. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100474. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 38359790 Free PMC article.
-
High risk Epstein-Barr virus variants characterized by distinct polymorphisms in the EBER locus are strongly associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2019 Jun 15;144(12):3031-3042. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32049. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30536939
-
Epstein-Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Oct 19;372(1732):20160270. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0270. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28893937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Associated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Emphasis on the Latent Gene Products of EBV.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Dec 20;59(1):2. doi: 10.3390/medicina59010002. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36676626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine in Human Oncogenic Herpesvirus Infections and Their Linked Cancers.Viruses. 2021 May 28;13(6):1014. doi: 10.3390/v13061014. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34071559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Slug inhibition increases radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line C666-1.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Apr;15(4):3477-3482. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5844. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29545871 Free PMC article.
-
A novel causal model for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Causes Control. 2022 Jul;33(7):1013-1018. doi: 10.1007/s10552-022-01582-x. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Cancer Causes Control. 2022. PMID: 35441278
-
The Long Non-Coding RNA ANRIL in Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;15(16):4160. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164160. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HLA-C*06:02-independent, gender-related association of PSORS1C3 and PSORS1C1/CDSN single-nucleotide polymorphisms with risk and severity of psoriasis.Mol Genet Genomics. 2018 Aug;293(4):957-966. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1435-4. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Mol Genet Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29589160 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tang LL, Chen WQ, Xue WQ, He YQ, Zheng RS, Zeng YX, Jia WH. Global trends in incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016;374:22–30. - PubMed
-
- Su SF, Han F, Zhao C, Chen CY, Xiao WW, Li JX, Lu TX. Long-term outcomes of early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:327–333. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

