Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes: Sentinels of the Mucosal Barrier
- PMID: 29221933
- PMCID: PMC8056148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2017.11.003
Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes: Sentinels of the Mucosal Barrier
Abstract
Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) are a large and diverse population of lymphoid cells that reside between the intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) that form the intestinal mucosal barrier. Although IEL biology has traditionally focused on T cells, recent studies have identified several subsets of T cell receptor (TCR)-negative IELs with intriguing properties. New insight into the development, homeostasis, and functions of distinct IEL subsets has recently been provided. Additional studies have revealed intricate interactions between different IEL subsets, reciprocal interactions between IELs and IECs, and communication of IELs with immune cells that reside outside the intestinal epithelium. We review here sentinel functions of IELs in the maintenance of the mucosal barrier integrity, as well as how dysregulated IEL responses can contribute to pathology.
Keywords: intestinal immunity; intestinal inflammation; intraepithelial lymphocytes; lymphocyte development; mucosal immunity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
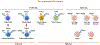
References
-
- Belkaid Y (2012) Mucosal immunity and Microbiome. In Fundamental Immunology (7 edn) (Paul WE ed), Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
-
- Cheroutre H (2004) Starting at the beginning: new perspectives on the biology of mucosal T cells. Annu Rev Immunol 22, 217–246 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki S et al. (1998) Low level of mixing of partner cells seen in extrathymic T cells in the liver and intestine of parabiotic mice: its biological implication. Eur J Immunol 28, 3719–3729 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

