Blood vitronectin is a major activator of LIF and IL-6 in the brain through integrin-FAK and uPAR signaling
- PMID: 29222114
- PMCID: PMC5826040
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.202580
Blood vitronectin is a major activator of LIF and IL-6 in the brain through integrin-FAK and uPAR signaling
Abstract
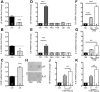
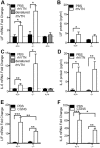
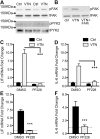
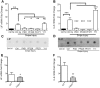
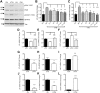
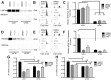
We defined how blood-derived vitronectin (VTN) rapidly and potently activates leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and pro-inflammatory interleukin 6 (IL-6) in vitro and after vascular injury in the brain. Treatment with VTN (but not fibrinogen, fibronectin, laminin-111 or collagen-I) substantially increased LIF and IL-6 within 4 h in C6-astroglioma cells, while VTN-/- mouse plasma was less effective than that from wild-type mice. LIF and IL-6 were induced by intracerebral injection of recombinant human (rh)VTN in mice, but induction seen upon intracerebral hemorrhage was less in VTN-/- mice than in wild-type littermates. In vitro, VTN effects were inhibited by RGD, αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrin-blocking peptides and antibodies. VTN activated focal adhesion kinase (FAK; also known as PTK2), whereas pharmacological- or siRNA-mediated inhibition of FAK, but not PYK2, reduced the expression of LIF and IL-6 in C6 and endothelial cells and after traumatic cell injury. Dominant-negative FAK (Y397F) reduced the amount of injury-induced LIF and IL-6. Pharmacological inhibition or knockdown of uPAR (also known as PLAUR), which binds VTN, also reduced cytokine expression, possibly through a common target of uPAR and integrins. We propose that VTN leakage into tissues promotes inflammation. Integrin-FAK signaling is therefore a novel IL-6 and LIF regulation mechanism relevant to the inflammation and stem cell fields.
Keywords: FAK; IL-6; Integrin; LIF; Vitronectin; uPAR.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new class of orthosteric uPAR·uPA small-molecule antagonists are allosteric inhibitors of the uPAR·vitronectin interaction.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):1521-34. doi: 10.1021/cb500832q. Epub 2015 Mar 31. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25671694 Free PMC article.
-
Vitronectin from brain pericytes promotes adult forebrain neurogenesis by stimulating CNTF.Exp Neurol. 2019 Feb;312:20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.11.002. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30408465 Free PMC article.
-
Vitronectin mitigates stroke-increased neurogenesis only in female mice and through FAK-regulated IL-6.Exp Neurol. 2020 Jan;323:113088. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113088. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31678139 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between urokinase receptor and vitronectin in cell adhesion and signalling.Eur J Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;87(8-9):617-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.02.003. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18353489 Review.
-
Structure, function and expression on blood and bone marrow cells of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, uPAR.Stem Cells. 1997;15(6):398-408. doi: 10.1002/stem.150398. Stem Cells. 1997. PMID: 9402652 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver vitronectin release into the bloodstream increases due to reduced vagal muscarinic signaling after cerebral stroke in female mice.Physiol Rep. 2022 May;10(9):e15301. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15301. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35531929 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SUMOylation in the neurovascular dysfunction after acquired brain injury.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 22;14:1125662. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1125662. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage migration is differentially regulated by fibronectin and laminin through altered adhesion and myosin II localization.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Feb 1;35(2):ar22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-04-0137. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38088893 Free PMC article.
-
Female-specific neuroprotection after ischemic stroke by vitronectin-focal adhesion kinase inhibition.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022 Oct;42(10):1961-1974. doi: 10.1177/0271678X221107871. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022. PMID: 35702047 Free PMC article.
-
PDIA3 inhibits mitochondrial respiratory function in brain endothelial cells and C. elegans through STAT3 signaling and decreases survival after OGD.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Dec 18;19(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00794-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34922569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banner L. R. and Patterson P. H. (1994). Major changes in the expression of the mRNAs for cholinergic differentiation factor/leukemia inhibitory factor and its receptor after injury to adult peripheral nerves and ganglia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 7109-7113. 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

