Classification and risk assessment in AML: integrating cytogenetics and molecular profiling
- PMID: 29222235
- PMCID: PMC6142605
- DOI: 10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.37
Classification and risk assessment in AML: integrating cytogenetics and molecular profiling
Abstract
In recent years, the composite molecular architecture in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has been mapped out. We now have a clearer understanding of the key genetic determinants, the major genetic interactions, and the broad order in which these mutations occur. The next impending challenge is to discern how these recent genomic discoveries define disease biology as well as how to use molecular markers to deliver patient-tailored clinical decision support.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

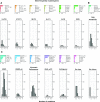
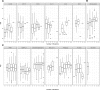
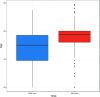
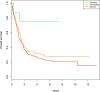
References
-
- Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukaemia: determination of prognostic significance of rarer recurring chromosomal abnormalities amongst 5,876 younger adult patients treated in the UK Medical Research Council trials. Br J Haematol. 2010;49:17. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al. ; European LeukemiaNet. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115(3):453-474. - PubMed
-
- Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016;127(20):2391-2405. - PubMed
-
- Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. . The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2008;114(5):937-952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

