Signaling pathways and immune evasion mechanisms in classical Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 29222272
- PMCID: PMC6142542
- DOI: 10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.310
Signaling pathways and immune evasion mechanisms in classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
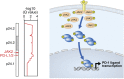
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is an unusual B-cell-derived malignancy in which rare malignant Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells are surrounded by an extensive but ineffective inflammatory/immune cell infiltrate. This striking feature suggests that malignant HRS cells escape immunosurveillance and interact with immune cells in the cancer microenvironment for survival and growth. We previously found that cHLs have a genetic basis for immune evasion: near-uniform copy number alterations of chromosome 9p24.1 and the associated PD-1 ligand loci, CD274/PD-L1 and PDCD1LG2/PD-L2, and copy number-dependent increased expression of these ligands. HRS cells expressing PD-1 ligands are thought to engage PD-1 receptor-positive immune effectors in the tumor microenvironment and induce PD-1 signaling and associated immune evasion. The genetic bases of enhanced PD-1 signaling in cHL make these tumors uniquely sensitive to PD-1 blockade.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: W.R.L. declares no competing financial interests. M.A.S. is on the Board of Directors or an advisory committee for Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) and Merck and has received research funding from BMS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signaling pathways and immune evasion mechanisms in classical Hodgkin lymphoma.Blood. 2017 Nov 23;130(21):2265-2270. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-781989. Blood. 2017. PMID: 29167175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-L1 and PD-L2 Genetic Alterations Define Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Predict Outcome.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug 10;34(23):2690-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.4482. Epub 2016 Apr 11. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27069084 Free PMC article.
-
Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma with Reduced β2M/MHC Class I Expression Is Associated with Inferior Outcome Independent of 9p24.1 Status.Cancer Immunol Res. 2016 Nov;4(11):910-916. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0201. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27737878 Free PMC article.
-
Mass cytometry of Hodgkin lymphoma reveals a CD4+ regulatory T-cell-rich and exhausted T-effector microenvironment.Blood. 2018 Aug 23;132(8):825-836. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-04-843714. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29880615 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and perspectives in the immunotherapy of Hodgkin lymphoma.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Nov;85:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28892775 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the mechanism of common inflammatory pathways in the pathogenesis and development of lymphoma.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2329130. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2329130. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 38489405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in postrelapse survival in classic Hodgkin lymphoma patients after experiencing therapy failure following auto-HCT.Blood Adv. 2020 Jan 14;4(1):47-54. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000736. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 31899797 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered T Cell Therapy in Lymphoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Mar 27;21(5):38. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0789-z. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30919158 Review.
-
Advances in CD30- and PD-1-targeted therapies for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):12206-12216. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34956447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene set-based identification of two immune subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma for guiding immune checkpoint blocking therapy.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 7;13:1000460. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1000460. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36276947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathas S, Hartmann S, Küppers R. Hodgkin lymphoma: pathology and biology. Semin Hematol. 2016;53(3):139-147. - PubMed
-
- Skinnider BF, Mak TW. The role of cytokines in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2002;99(12):4283-4297. - PubMed
-
- Aldinucci D, Lorenzon D, Cattaruzza L, et al. . Expression of CCR5 receptors on Reed-Sternberg cells and Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines: involvement of CCL5/Rantes in tumor cell growth and microenvironmental interactions. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(4):769-776. - PubMed
-
- Fischer M, Juremalm M, Olsson N, et al. . Expression of CCL5/RANTES by Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells and its possible role in the recruitment of mast cells into lymphomatous tissue. Int J Cancer. 2003;107(2):197-201. - PubMed
-
- Ishida T, Ishii T, Inagaki A, et al. . Specific recruitment of CC chemokine receptor 4-positive regulatory T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma fosters immune privilege. Cancer Res. 2006;66(11):5716-5722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

