Sodium salt medium-chain fatty acids and Bacillus-based probiotic strategies to improve growth and intestinal health of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata)
- PMID: 29226031
- PMCID: PMC5719961
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4001
Sodium salt medium-chain fatty acids and Bacillus-based probiotic strategies to improve growth and intestinal health of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata)
Abstract
Background: The increased demand for fish protein has led to the intensification of aquaculture practices which are hampered by nutritional and health factors affecting growth performance. To solve these problems, antibiotics have been used for many years in the prevention, control and treatment against disease as well as growth promoters to improve animal performance. Nowadays, the use of antibiotics in the European Union and other countries has been completely or partially banned as a result of the existence of antibiotic cross-resistance. Therefore, a number of alternatives, including enzymes, prebiotics, probiotics, phytonutrients and organic acids used alone or in combination have been proposed for the improvement of immunological state, growth performance and production in livestock animals. The aim of the present study was to evaluate two commercially available feed additives, one based on medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs) from coconut oil and another with a Bacillus-based probiotic, in gilthead sea bream (GSB, Sparus aurata), a marine farmed fish of high value in the Mediterranean aquaculture.
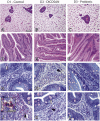
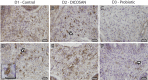
Methods: The potential benefits of adding two commercial feed additives on fish growth performance and intestinal health were assessed in a 100-days feeding trial. The experimental diets (D2 and D3) were prepared by supplementing a basal diet (D1) with MCFAs in the form of a sodium salt of coconut fatty acid distillate (DICOSAN®; Norel, Madrid, Spain), rich on C-12, added at 0.3% (D2) or with the probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CECT 5940, added at 0.1% (D3). The study integrated data on growth performance, blood biochemistry, histology and intestinal gene expression patterns of selected markers of intestinal function and architecture.
Results: MCFAs in the form of a coconut oil increased feed intake, growth rates and the surface of nutrient absorption, promoting the anabolic action of the somatotropic axis. The probiotic (D3) induced anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects with changes in circulating cortisol, immunoglobulin M, leukocyte respiratory burst, and mucosal expression levels of cytokines, lymphocyte markers and immunoglobulin T.
Discussion: MCFA supplementation showed positive effects on GSB growth and intestinal architecture acting mainly in the anterior intestine, where absorption takes place. The probiotic B. amyloliquefaciens CECT 5940 exhibited key effects in the regulation of the immune status inducing anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects which can be potentially advantageous upon infection or exposure to other stressors. The potential effects of these feed additives in GSB are very promising to improve health and disease resistance in aquaculture.
Keywords: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; DICOSAN; Intestinal health; Medium-chain fatty acid; Probiotic; Teleost.
Conflict of interest statement
Álvaro Ortiz is an employee of Evonik Nutrition and Care GmbH, Hanau-Wolfgang, Germany and Mónica Puyalto is an employee of NOREL S.A., Madrid, Spain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of a specific composition of short- and medium-chain fatty acid 1-Monoglycerides on growth performances and gut microbiota of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata).PeerJ. 2018 Jul 31;6:e5355. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5355. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 30083467 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Butyrate Helps to Restore the Intestinal Status of a Marine Teleost (Sparus aurata) Fed Extreme Diets Low in Fish Meal and Fish Oil.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 29;11(11):e0166564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166564. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27898676 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary NEXT ENHANCE®150 on growth performance and expression of immune and intestinal integrity related genes in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 May;44(1):117-28. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.01.039. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25681752
-
Medium-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides as feed additives for pig production: towards gut health improvement and feed pathogen mitigation.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020 Apr 23;11:44. doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00446-1. eCollection 2020. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32337029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of prebiotics in aquaculture as immunostimulants. Effects on immune system of Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Jul;54:172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 10. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27074444 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics and Nutrition Drive the Gut Microbiota Succession and Host-Transcriptome Interactions through the Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Production Cycle.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;11(12):1744. doi: 10.3390/biology11121744. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552254 Free PMC article.
-
Autochthonous Probiotics Alleviate the Adverse Effects of Dietary Histamine in Juvenile Grouper (Epinephelus coioides).Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 7;12:792718. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.792718. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34950122 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression Analysis of Sirtuins and Related Metabolic Biomarkers in Juveniles of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) With Differences in Growth Performance.Front Physiol. 2018 Jun 5;9:608. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00608. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29922168 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional impact of nano zeolite, probiotic, and fatty acids as feed additives on health status of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 20;13(1):22740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50034-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38123621 Free PMC article.
-
Current Development and Future Application Prospects of Plants-Derived Polyphenol Bioactive Substance Curcumin as a Novel Feed Additive in Livestock and Poultry.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 7;23(19):11905. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911905. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233207 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aly SM, Mohamed MF, John G. Effect of probiotics on the survival, growth and challenge infection in Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) Aquaculture Research. 2008;39:647–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.01932.x. - DOI
-
- Bakke-McKellep AM, McL Press C, Baeverfjord G, Krogdahl Å, Landsverk T. Changes in immune and enzyme histochemical phenotypes of cells in the intestinal mucosa of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., with soybean meal-induced enteritis. Journal of Fish Diseases. 2000;23:115–127. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2761.2000.00218.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

