Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics identifies phenylalanine as a novel predictor of incident heart failure hospitalisation: results from PROSPER and FINRISK 1997
- PMID: 29226610
- PMCID: PMC5947152
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.1076
Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics identifies phenylalanine as a novel predictor of incident heart failure hospitalisation: results from PROSPER and FINRISK 1997
Abstract
Aims: We investigated the association between quantified metabolite, lipid and lipoprotein measures and incident heart failure hospitalisation (HFH) in the elderly, and examined whether circulating metabolic measures improve HFH prediction.
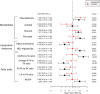
Methods and results: Overall, 80 metabolic measures from the PROspective Study of Pravastatin in the Elderly at Risk (PROSPER) trial were measured by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (n = 5341; 182 HFH events during 2.7-year follow-up). We repeated the work in FINRISK 1997 (n = 7330; 133 HFH events during 5-year follow-up). In PROSPER, the circulating concentrations of 13 metabolic measures were found to be significantly different in those who were later hospitalised for heart failure after correction for multiple comparisons. These included creatinine, phenylalanine, glycoprotein acetyls, 3-hydroxybutyrate, and various high-density lipoprotein measures. In Cox models, two metabolites were associated with risk of HFH after adjustment for clinical risk factors and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP): phenylalanine [hazard ratio (HR) 1.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.10-1.53; P = 0.002] and acetate (HR 0.81, 95% CI 0.68-0.98; P = 0.026). Both were retained in the final model after backward elimination. Compared to a model with established risk factors and NT-proBNP, this model did not improve the C-index but did improve the overall continuous net reclassification index (NRI 0.21; 95% CI 0.06-0.35; P = 0.007) due to improvement in classification of non-cases (NRI 0.14; 95% CI 0.12-0.17; P < 0.001). Phenylalanine was replicated as a predictor of HFH in FINRISK 1997 (HR 1.23, 95% CI 1.03-1.48; P = 0.023).
Conclusion: Our findings identify phenylalanine as a novel predictor of incident HFH, although prediction gains are low. Further mechanistic studies appear warranted.
Keywords: Advanced lipoprotein profiling; FINRISK; Heart failure; Metabolomics; PROSPER; Phenylalanine.
© 2017 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Predicting heart failure: one size does not fit all.Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Apr;20(4):674-676. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1120. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29333673 No abstract available.
References
-
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez‐Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Køber L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, Popescu BA, Rønnevik PK, Rutten FH, Schwitter J, Seferovic P, Stepinska J, Trindade PT, Voors AA, Zannad F, Zeiher A. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC . Eur J Heart Fail 2012;14:803–869. - PubMed
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, Jessup M, Konstam MA, Mancini DM, Michl K, Oates JA, Rahko PS, Silver MA, Stevenson LW, Yancy CW. 2009 Focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Developed in collaboration with the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation . J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:e1–e90. - PubMed
-
- Hunt SA, Baker DW, Chin MH, Cinquegrani MP, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, Goldstein S, Gregoratos G, Jessup ML, Noble RJ, Packer M, Silver MA, Stevenson LW, Gibbons RJ, Antman EM, Alpert JS, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gregoratos G, Jacobs AK, Hiratzka LF, Russell RO, Smith SC Jr. ACC/AHA Guidelines for the evaluation and management of chronic heart failure in the adult: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Revise the 1995 Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Heart Failure): developed in collaboration with the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation; endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 2001;104:2996–3007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

