Reward System Activation in Response to Alcohol Advertisements Predicts College Drinking
- PMID: 29227227
- PMCID: PMC5894856
- DOI: 10.15288/jsad.2018.79.29
Reward System Activation in Response to Alcohol Advertisements Predicts College Drinking
Abstract
Objective: In this study, we assess whether activation of the brain's reward system in response to alcohol advertisements is associated with college drinking. Previous research has established a relationship between exposure to alcohol marketing and underage drinking. Within other appetitive domains, the relationship between cue exposure and behavioral enactment is known to rely on activation of the brain's reward system. However, the relationship between neural activation to alcohol advertisements and alcohol consumption has not been studied in a nondisordered population.
Method: In this cross-sectional study, 53 college students (32 women) completed a functional magnetic resonance imaging scan while viewing alcohol, food, and control (car and technology) advertisements. Afterward, they completed a survey about their alcohol consumption (including frequency of drinking, typical number of drinks consumed, and frequency of binge drinking) over the previous month.
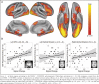
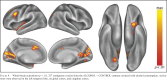
Results: In 43 participants (24 women) meeting inclusion criteria, viewing alcohol advertisements elicited activation in the left orbitofrontal cortex and bilateral ventral striatum-regions of the reward system that typically activate to other appetitive rewards and relate to consumption behaviors. Moreover, the level of self-reported drinking correlated with the magnitude of activation in the left orbitofrontal cortex.
Conclusions: Results suggest that alcohol cues are processed within the reward system in a way that may motivate drinking behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Back to the Future . . . or . . . Is That All There Is? A Commentary on Courtney et al. (2018).J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2018 Jan;79(1):39-40. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29227228 No abstract available.
-
Brain Reward Responses Are Behaviorally Relevant: The Authors Respond.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2018 Jan;79(1):41-42. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2018.79.41. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29227229 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Beer Institute. Advertising & Marketing Code. n.d Retrieved from http://www.beerinstitute.org/responsibility/advertising-marketing-code/
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

