Endothelial permeability, LDL deposition, and cardiovascular risk factors-a review
- PMID: 29228169
- PMCID: PMC7729208
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvx226
Endothelial permeability, LDL deposition, and cardiovascular risk factors-a review
Abstract
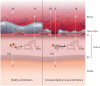
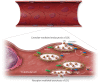
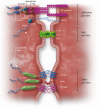
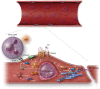
Early atherosclerosis features functional and structural changes in the endothelial barrier function that affect the traffic of molecules and solutes between the vessel lumen and the vascular wall. Such changes are mechanistically related to the development of atherosclerosis. Proatherogenic stimuli and cardiovascular risk factors, such as dyslipidaemias, diabetes, obesity, and smoking, all increase endothelial permeability sharing a common signalling denominator: an imbalance in the production/disposal of reactive oxygen species (ROS), broadly termed oxidative stress. Mostly as a consequence of the activation of enzymatic systems leading to ROS overproduction, proatherogenic factors lead to a pro-inflammatory status that translates in changes in gene expression and functional rearrangements, including changes in the transendothelial transport of molecules, leading to the deposition of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and the subsequent infiltration of circulating leucocytes in the intima. In this review, we focus on such early changes in atherogenesis and on the concept that proatherogenic stimuli and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, by altering the endothelial barrier properties, co-ordinately trigger the accumulation of LDL in the intima and ultimately plaque formation.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular risk factors; Endothelium; Vascular permeability.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2017. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Smoking and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction and early atherogenesis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Mar;34(3):509-15. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.300156. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24554606 Review.
-
Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis: the role of microRNAs in arterial remodeling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Sep;64:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23797034 Review.
-
Highlight on Endothelial Activation and Beyond.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Dec;38(12):e198-e201. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312054. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30571176 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis].Orv Hetil. 2015 Jul 12;156(28):1115-9. doi: 10.1556/650.2015.30201. Orv Hetil. 2015. PMID: 26149503 Review. Hungarian.
-
Patient-specific computational modeling of subendothelial LDL accumulation in a stenosed right coronary artery: effect of hemodynamic and biological factors.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Jun 1;304(11):H1455-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00539.2012. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23504178
Cited by
-
PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021 Dec;18(12):809-823. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00569-6. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34127848 Review.
-
Homocysteine, Vitamins B6 and Folic Acid in Experimental Models of Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure-How Strong Is That Link?Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 1;12(4):536. doi: 10.3390/biom12040536. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TET1s deficiency exacerbates oscillatory shear flow-induced atherosclerosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Feb 28;18(5):2163-2180. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.69281. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342333 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic Fibrosis in Insulin-Sensitive Mice with Endothelial Cell-Specific Deletion of Ceacam1 Gene.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 14;23(8):4335. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084335. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457157 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Sirolimus and Magnesium on Primary Human Coronary Endothelial Cells: An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2930. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032930. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Caterina R, Libby P. Endothelial Dysfunctions in Vascular Disease. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing, 2007.
-
- Skalen K, Gustafsson M, Rydberg EK, Hulten LM, Wiklund O, Innerarity TL, Boren J. Subendothelial retention of atherogenic lipoproteins in early atherosclerosis. Nature 2002;417:750–754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

