The epidemiology of stroke in Africa: A systematic review of existing methods and new approaches
- PMID: 29228472
- PMCID: PMC5777902
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13152
The epidemiology of stroke in Africa: A systematic review of existing methods and new approaches
Abstract
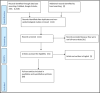
Accurate epidemiological surveillance of the burden of stroke is direly needed to facilitate the development and evaluation of effective interventions in Africa. The authors therefore conducted a systematic review of the methodology of stroke epidemiological studies conducted in Africa from 1970 to 2017 using gold standard criteria obtained from landmark epidemiological publications. Of 1330 articles extracted, only 50 articles were eligible for review grouped under incidence, prevalence, case-fatality, health-related quality of life, and disability-adjusted life-years studies. Because of various challenges, no study fulfilled the criteria for an excellent stroke incidence study. The relatively few stroke epidemiology studies in Africa have significant methodological flaws. Innovative approaches leveraging available information and communication technology infrastructure are recommended to facilitate rigorous epidemiological studies for accurate stroke surveillance in Africa.
Keywords: African; epidemiology; incidence; prevalence; stroke; surveillance.
©2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global Health Observatory (GHO) data. Raised blood pressure. Situations and trends. www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/blood_pressure_prevalence_text/en/. Accessed July 31, 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical