Biomarker significance of plasma and tumor miR-21, miR-221, and miR-106a in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 29228567
- PMCID: PMC5722519
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18236
Biomarker significance of plasma and tumor miR-21, miR-221, and miR-106a in osteosarcoma
Abstract
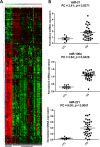
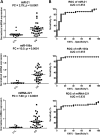
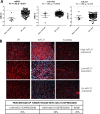
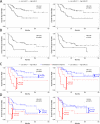
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant bone tumor in children and young adults. Despite the use of surgery and multi-agent chemotherapy, osteosarcoma patients who have a poor response to chemotherapy or develop relapses have a dismal outcome. Identification of biomarkers for active disease may help to monitor tumor burden, detect early relapses, and predict prognosis in these patients. In this study, we examined whether circulating miRNAs can be used as biomarkers in osteosarcoma patients. We performed genome-wide miRNA profiling on a discovery cohort of osteosarcoma and control plasma samples. A total of 56 miRNAs were upregulated and 164 miRNAs were downregulated in osteosarcoma samples when compared to control plasma samples. miR-21, miR-221 and miR-106a were selected for further validation based on their known biological importance. We showed that all three circulating miRNAs were expressed significantly higher in osteosarcoma samples than normal samples in an independent cohort obtained from the Children's Oncology Group. Furthermore, we demonstrated that miR-21 was expressed significantly higher in osteosarcoma tumors compared with normal bone controls. More importantly, lower expressions of miR-21 and miR-221, but not miR-106a, significantly correlated with a poor outcome. In conclusion, our results indicate that miR-21, miR-221 and miR-106a were elevated in the circulation of osteosarcoma patients, whereas tumor expressions of miR-21 and miR-221 are prognostically significant. Further investigation of these miRNAs may lead to a better prognostic method and potential miRNA therapeutics for osteosarcoma.
Keywords: biomarker; miRNA; osteosarcoma; plasma; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a plasma four-microRNA panel as potential noninvasive biomarker for osteosarcoma.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0121499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121499. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775010 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of tumor miR-21, miR-221, miR-143, and miR-106a as biomarkers in patients with osteosarcoma.Int J Biol Markers. 2019 Jun;34(2):184-193. doi: 10.1177/1724600819843537. Epub 2019 May 14. Int J Biol Markers. 2019. PMID: 31084400
-
Clinical significance of circulating miR-25-3p as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in osteosarcoma.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33375-33392. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16498. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28380419 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs from the miR-106a-363 cluster on chromosome X as novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jul;170(2):257-270. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4757-3. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29557526 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Canine Osteosarcoma: A New Future?Vet Sci. 2020 Sep 30;7(4):146. doi: 10.3390/vetsci7040146. Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33008041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Circulating Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Tumor Monitoring in Pediatric Sarcomas: Recent Advances and Future Directions.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 16;14(10):1306. doi: 10.3390/biom14101306. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Common Solid Tumors: Focus on Lung, Breast, Prostate Cancers, and Osteosarcoma.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 11;8(10):1661. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101661. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31614612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-associated repetitive element DNAs as candidate osteosarcoma biomarkers.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 8;11(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77398-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33420117 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomics reveals cellular subtypes and molecular features associated with osteosarcoma prognosis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 17;25(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13714-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39962461 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway Analysis for Cancer Research and Precision Oncology Applications.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1361:143-161. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-91836-1_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35230687
References
-
- Dorfman HD, Czerniak B. Bone cancers. Cancer. 1995;75:203–10. - PubMed
-
- Link MP, Goorin AM, Miser AW, Green AA, Pratt CB, Belasco JB, Pritchard J, Malpas JS, Baker AR, Kirkpatrick JA, Ayala AG, Shuster JJ, Abelson HT, et al. The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse-free survival in patients with osteosarcoma of the extremity. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1600–6. - PubMed
-
- Szendroi M, Papai Z, Koos R, Illes T. Limb-saving surgery, survival, and prognostic factors for osteosarcoma: the Hungarian experience. J Surg Oncol. 2000;73:87–94. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

