Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1: predictive and prognostic significance in cancer
- PMID: 29228642
- PMCID: PMC5722594
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18311
Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1: predictive and prognostic significance in cancer
Abstract
The membrane-bound molecules programmed death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 (PD-1/PD-L1) belong to the immune checkpoint pathway. PD-1 pathway downregulates effector T cells in immune response, thereby causing immune suppression. Recent studies have revealed that membrane-bound PD-1 and PD-L1 also have soluble forms. These soluble forms increase the complexity and diversity of the composition and function of the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway. However, the exact roles of these molecules remain unknown. The objective of this systematic review was to elucidate the biological significance of soluble PD-1/PD-L1 in human cancers and evaluate whether they are potential diagnostic, therapeutic, or prognostic biomarkers. We expect to provide new clues for future research on soluble PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in human malignant tumors.
Keywords: PD-1; PD-L1; biomarker; soluble; tumor immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article is reported.
Figures
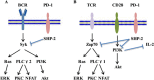
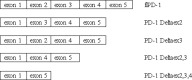

References
-
- Hamanishi J, Konishi I. [Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint signal - a new treatment strategy for cancer] Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2014;41:1071–76. - PubMed
-
- Ge Y, Xi H, Ju S, Zhang X. Blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint during DC vaccination induces potent protective immunity against breast cancer in hu-SCID mice. Cancer Lett. 2013;336:253–59. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

