Impact of anger emotional stress before pregnancy on adult male offspring
- PMID: 29228731
- PMCID: PMC5716771
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22007
Impact of anger emotional stress before pregnancy on adult male offspring
Abstract
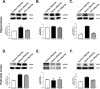
Previous studies have reported that maternal chronic stress or depression is linked to an increased risk of affective disorders in progeny. However, the impact of maternal chronic stress before pregnancy on the progeny of animal models is unknown. We investigated the behaviors and the neurobiology of 60-day-old male offspring of female rats subjected to 21 days of resident-intruder stress before pregnancy. An anger stressed parental rat model was established using the resident-intruder paradigm and it was evaluated using behavioral tests. Anger stressed maternal rats showed a significant increase in locomotion and aggression but a reduction in sucrose preference. Offspring subjected to pre-gestational anger stress displayed enhanced aggressive behaviors, reduced anxiety, and sucrose preference. Further, offspring subjected to pre-gestational stress showed significant impairments in the recognition index (RI) on the object recognition test and the number of platform crossings in the Morris water maze test. The monoaminergic system was significantly altered in pre-gestationally stressed offspring, and the expression of phosphorylated cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein (P-CREB), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and serotonin transporter (SERT) levels in pre-gestational stressed offspring were altered in some brain regions. Fluoxetine was used to treat pre-gestational stressed maternal rats and it significantly reduced the changes caused by stress, as evidenced by both behaviors and neural biochemical indexes in the offspring in some but not all cases. These findings suggest that anger stress before pregnancy could induce aggressive behaviors, cognitive deficits, and neurobiological alterations in offspring.
Keywords: aggressive behavior test; anger emotion; monoamine neurotransmitters; resident intruder paradigm; stress before pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No author has any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
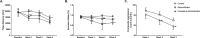
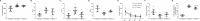


Similar articles
-
Social defeat stress before pregnancy induces depressive-like behaviours and cognitive deficits in adult male offspring: correlation with neurobiological changes.BMC Neurosci. 2018 Oct 16;19(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12868-018-0463-7. BMC Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30326843 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal nicotine intoxication before pregnancy induces depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors as well as cognitive deficits in male offspring and correlates with neurobiological changes.Brain Behav. 2023 Jul;13(7):e3052. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3052. Epub 2023 May 9. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37161637 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and neurobiological studies on the male progeny of maternal rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress before pregnancy.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Jan 22;469(2):278-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.12.017. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20018228
-
Prenatal stress and early adoption effects on benzodiazepine receptors and anxiogenic behavior in the adult rat brain.Synapse. 2006 Dec 15;60(8):609-18. doi: 10.1002/syn.20336. Synapse. 2006. PMID: 17019679
-
Effects of gestational stress: 1. Evaluation of maternal and juvenile offspring behavior.Brain Res. 2008 Jun 5;1213:98-110. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.03.035. Epub 2008 Apr 1. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18456246
Cited by
-
Pre-reproductive stress in adolescent female rats alters oocyte microRNA expression and offspring phenotypes: pharmacological interventions and putative mechanisms.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Feb 5;11(1):113. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01220-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33547270 Free PMC article.
-
Social defeat stress before pregnancy induces depressive-like behaviours and cognitive deficits in adult male offspring: correlation with neurobiological changes.BMC Neurosci. 2018 Oct 16;19(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12868-018-0463-7. BMC Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30326843 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological modulation of the behavioral effects of social defeat in memory and learning in male mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Sep;236(9):2797-2810. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05256-6. Epub 2019 May 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31049607
-
Associations of Maternal Trait Anger Expression and Lifetime Traumatic and Non-traumatic Experiences with Preterm Birth.Matern Child Health J. 2021 Apr;25(4):635-644. doi: 10.1007/s10995-020-03026-x. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Matern Child Health J. 2021. PMID: 33206302 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effect of fluoxetine, escitalopram, and sertraline, on the level of BDNF and depression in preclinical and clinical studies: a systematic review.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;80(7):983-1016. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03680-y. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38558317
References
-
- Foster CJ, Garber J, Durlak JA. Current and past maternal depression, maternal interaction behaviors, and children's externalizing and internalizing symptoms. Journal of abnormal child psychology. 2008;36:527–537. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Zhang L, Huang Q. Differential expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in the hippocampus of rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress. Behavioural brain research. 2009;205:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Hobel C, Culhane J. Role of psychosocial and nutritional stress on poor pregnancy outcome. The Journal of nutrition. 2003;133:1709S–1717S. - PubMed
-
- Altarac M, Strobino D. Abuse during pregnancy and stress because of abuse during pregnancy and birthweight. Journal of the American Medical Women's Association. 2002;57:208–214. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

