Combination of berberine and evodiamine inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption in high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic rats
- PMID: 29228954
- PMCID: PMC5725942
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0628-x
Combination of berberine and evodiamine inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption in high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic rats
Abstract
Background: Hyperlipidemia characterized of elevated serum lipid levels is a prevalent disease frequently resulting in cardiovascular disease (CVD). Berberine and evodiamine are herbal products of traditional Chinese herb Coptis chinensis and Evodia rutaecarpa, which are indicated to exert regulation of lipid metabolism. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the lipid-lowering effect of berberine and evodiamine combination in hyperlipidemic rats.
Method: The rat model of hyperlipidemia was established by providing high-fat-diet (HFD) for 4 weeks. Berberine (BB), evodiamine (EV), and their combination (BB + EV) were orally administered to HFD induced rats for 4 weeks. Body weight, food utilization, histopathology of liver tissues, lipid profiles of serum and liver were measured. Gas chromatography (GC) analysis was applied to examine the level of plasma total cholesterol and ß- Sitosterol (BS) to estimate cholesterol absorption activity. Furthermore, intestinal NPC1L1, ACAT2, and ApoB48 protein expressions were evaluated by immunohistochemical assay.
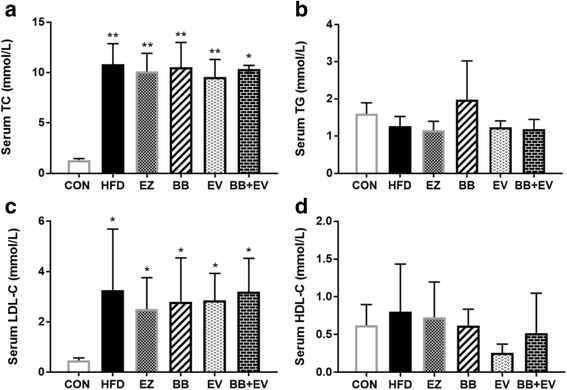
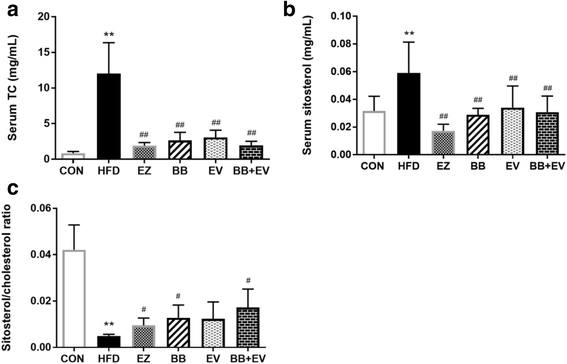
Result: According to the results, decreased levels of serum cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), as well as hepatic TC were showed in hyperlipidemic rats treated by combination of berberine and evodiamine. GC analysis indicated that the elevated plasma BS was significantly ameliorated by BB, EV, and BB + EV. In addition, immunohistochemical analysis revealed that BB + EV treatment down-regulated the expressions of intestinal NPC1L1 and ACAT2, and ApoB48 in HFD induced rats.
Conclusion: Based on the above results, combination of berberine and evodiamine exerted a promising preventive effect on hyperlipidemia, partially through inhibiting intestinal absorption of cholesterol.
Keywords: ACAT2; ApoB48; Berberine; Cholesterol absorption; Evodiamine; Hyperlipidemia; NPC1L1.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
The animal protocol was approved by the Animal Ethical Committee of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Sichuan, China).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors state that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

